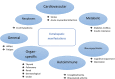
HCV Extrahepatic Manifestations
- PMID: 31293918
- PMCID: PMC6609844
- DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2018.00049
HCV Extrahepatic Manifestations
Abstract
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) has been shown to affect many tissues other than liver. However, of the many extrahepatic manifestations (EMs) that have been associated with HCV, including cryoglobulinemia, lymphoma, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes and neurological disorders, only a few have been shown to be directly related to HCV infection of extrahepatic tissues. HCV-triggered immune-mediated mechanisms account for most of the EMs. It is estimated that up to 74% of patients with chronic hepatitis C can develop at least one EM. All HCV patients with EMs should be considered for antiviral therapy, although not all will resolve with sustained virological response.
Keywords: B cell lymphomas; Direct-acting antivirals; Extrahepatic manifestations; Hepatic stellate cells; Hepatitis C virus; TGF-β-dependent signaling pathway; pancreatic B cell.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interests related to this publication.
Figures
References
-
- Austria AM, Ninčević V, Wu GY. Smolic M, Vcev A, Wu GY, editors. A brief update on the treatment of hepatitis C. Update on hepatitis C. IntechOpen. 2017:3–16. doi: 10.5772/intechopen.70685. - DOI
-
- Virovic Jukic L, Kralj D. Smolic M, Vcev A, Wu GY, editors. Extrahepatic Manifestations of Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Update on hepatitis C. IntechOpen. 2017:111–124. doi: 10.5772/intechopen.70728. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources