Rotundic Acid Induces DNA Damage and Cell Death in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Through AKT/mTOR and MAPK Pathways
- PMID: 31293977
- PMCID: PMC6606729
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00545
Rotundic Acid Induces DNA Damage and Cell Death in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Through AKT/mTOR and MAPK Pathways
Abstract
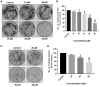
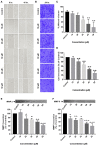
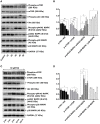
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the fourth largest cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide with limited therapeutic interventions. Renewed interest in natural products as drug leads has resulted in a paradigm shift toward the rapid screening of medicinal plants for the discovery of new chemical entities. Rotundic acid (RA), a plant-derived triterpenoid, has been anecdotally reported to possess anti-inflammatory and cardio-protective abilities. The present study highlights the anti-cancer efficacy of RA on HCC in vitro and in vivo. The inhibitory effects of RA on HCC cell viability was determined by MTT. Soft agar colony formation and clonogenic assays also showed that RA inhibited HCC cell proliferation. Flow cytometry, confocal, and western blot results further indicated that RA induced cell cycle arrest, DNA damage, and apoptosis by modulating the AKT/mTOR and MAPK pathways. Besides the suppression of migration and invasion, tube formation and VEGF-ELISA revealed the anti-angiogenic abilities of RA on HCC. Moreover, RA also inhibited tumor growth in a HepG2 xenograft mouse model. To our best knowledge, this is the first extensive study of the anticancer activity of RA on HCC. The results demonstrate that RA could be a potential drug candidate for HCC treatment.
Keywords: DNA damage; anti-angiogenesis; apoptosis; hepatocellular carcinoma; rotundic acid.
Figures






References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

