Intrahepatic Gallbladder
- PMID: 31293994
- PMCID: PMC6601687
- DOI: 10.12890/2019_001123
Intrahepatic Gallbladder
Abstract
Gallbladders have been reported in various ectopic locations. An intrahepatic gallbladder is one where the gallbladder lies within the liver parenchyma or has a subcapsular location along the anterior inferior right lobe of the liver. Intrahepatic gallbladders can have impaired function leading to the formation of gallbladder stones. We present the case of a 57-year-old man who was found to have an intrahepatic gallbladder which was not detected before a retrograde open cholecystectomy was carried out without intra-operative or postoperative complications. Awareness of ectopic gallbladders and their recognition allows proper intra-operative planning.
Learning points: Gallbladder disease in intrahepatic gallbladders poses an additional surgical risk for patients and complicates cholecystectomy or other biliary procedures.Awareness of this rare entity as well as optimum management will prevent patient morbidity and improve outcome.Preoperative MR cholangiopancreatographyis recommended if an intrahepatic gallbladder is identified on ultrasound or CT.Expert hepatobiliary surgeon involvement as well as an intra-operative cholangiogram is recommended in complex cases with abnormal biliary or hepatic vascular anatomy.
Keywords: Gallbladder; cholecystectomy; intrahepatic gallbladder.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interests: The Authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Figures
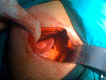
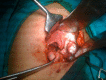

References
-
- Faure JP, Doucet C, Scepi M, Rigoard P, Carretier M, Richer JP. Abnormalities of the gallbladder, clinical effects. Surg Radiol Anat. 2008;30(4):285–290. - PubMed
-
- Lobo SW, Menezes RG, Mamata S, Baral P, Kanchan T, Hunnargi SA, et al. Ectopic partial intrahepatic gall bladder with cholelithiasis--a rare anomaly. Nepal Med Coll J. 2007;9(4):286–288. - PubMed
-
- Alkatout I, Henopp T, Moritz JD, Nikischin W, Klöppel G, Engler S. Extraabdominal malposition of the gallbladder. J Pediatr Surg. 2008;43(11):e41–e44. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
