The prevalence of cardiovascular disease and antidiabetes treatment characteristics among a large type 2 diabetes population in the United States
- PMID: 31294089
- PMCID: PMC6613222
- DOI: 10.1002/edm2.76
The prevalence of cardiovascular disease and antidiabetes treatment characteristics among a large type 2 diabetes population in the United States
Abstract
Objectives: The purpose of this study was to assess atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) prevalence, antidiabetes medication usage and physician specialty encounters among individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in the United States during 2015.
Design: Retrospective, cross-sectional analysis.
Patients: Adults with T2DM in a large US administrative claims database. Patients were divided into ASCVD and non-ASCVD groups. Subgroup analyses were conducted for three age groups (18-44, 45-64 and 65+ years).
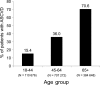
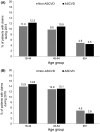
Results: Of 1 202 596 patients with T2DM, 45.2% had established ASCVD. About 40% of T2DM patients with ASCVD had visited a cardiologist during 2015, compared to 11% in the non-ASCVD group. The use of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) and sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT-2is) was low overall (<12%), and even lower in the ASCVD group (<9%). The prevalence of ASCVD was 15%, 36% and 71% in the 18-44, 45-64 and 65+ year age groups, respectively. GLP-1RA and SGLT-2i use was ≤5% in the 65+ subgroup, regardless of ASCVD status.
Conclusions: These real-world data showed a high prevalence of ASCVD among T2DM patients, and confirmed, as a baseline assessment, low use of GLP-1RAs and SGLT-2is in these at-risk patients prior to the 2017 American Diabetes Association guidelines recommending use of agents with proven cardiovascular benefits.
Keywords: GLP‐1RA; SGLT‐2i; atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; epidemiology; real‐world; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Conflict of interest statement
W. Weng, R. Ganguly, M. Hersloev, J. Brett and T. Hobbs are current employees of Novo Nordisk Inc., the funding body for this study. Y. Tian was a contracted employee of Novo Nordisk Inc., the funding body for this study, during study conduct. S. X. Kong was an employee of Novo Nordisk, Inc., during study conduct.
Figures
References
-
- Weng W, Liang Y, Kimball ES, et al. Decreasing incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus in the United States, 2007‐2012: epidemiologic findings from a large US claims database. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2016;117:111‐118. - PubMed
-
- Iglay K, Hannachi H, Joseph Howie P, et al. Prevalence and co‐prevalence of comorbidities among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr Med Res Opin. 2016;32(7):1243‐1252. - PubMed
-
- American Diabetes Association . Cardiovascular disease and risk management. Sec. 9. In Standards of medical care in diabetes 2017. Diabetes Care. 2017;40(Suppl 1):S75‐S87. - PubMed
-
- Green JB, Bethel MA, Armstrong PW, et al. Effect of sitagliptin on cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:232‐242. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

