An overview of the antimicrobial resistance mechanisms of bacteria
- PMID: 31294229
- PMCID: PMC6604941
- DOI: 10.3934/microbiol.2018.3.482
An overview of the antimicrobial resistance mechanisms of bacteria
Abstract
Resistance to antimicrobial agents has become a major source of morbidity and mortality worldwide. When antibiotics were first introduced in the 1900's, it was thought that we had won the war against microorganisms. It was soon discovered however, that the microorganisms were capable of developing resistance to any of the drugs that were used. Apparently most pathogenic microorganisms have the capability of developing resistance to at least some antimicrobial agents. The main mechanisms of resistance are: limiting uptake of a drug, modification of a drug target, inactivation of a drug, and active efflux of a drug. These mechanisms may be native to the microorganisms, or acquired from other microorganisms. Understanding more about these mechanisms should hopefully lead to better treatment options for infective diseases, and development of antimicrobial drugs that can withstand the microorganisms attempts to become resistant.
Keywords: CRE; ESBL; MRSA; antimicrobial resistance; β-lactamase.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The author declares that there are no conflicts of interest in this paper.
Figures
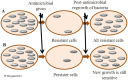


References
-
- World Health Organization. World Health Statistics 2014. 2014.
-
- World Health Organization. Global action plan on antimicrobial resistance. 2015. - PubMed
-
- Griffith M, Postelnick M, Scheetz M. Antimicrobial stewardship programs: methods of operation and suggested outcomes. Expert Rev Anti-Infe. 2012;10:63–73. - PubMed
-
- Yu VL. Guidelines for hospital-acquired pneumonia and health-care-associated pneumonia: a vulnerability, a pitfall, and a fatal flaw. Lancet Infect Dis. 2011;11:248–252. - PubMed
-
- Goossens H. Antibiotic consumption and link to resistance. Clin Microbiol Infec. 2009;15 3:12–15. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
