Microbial activity in Martian analog soils after ionizing radiation: implications for the preservation of subsurface life on Mars
- PMID: 31294232
- PMCID: PMC6604939
- DOI: 10.3934/microbiol.2018.3.541
Microbial activity in Martian analog soils after ionizing radiation: implications for the preservation of subsurface life on Mars
Abstract
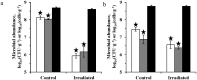
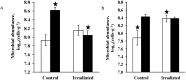
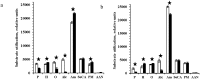
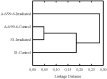
At present, the surface of Mars is affected by a set of factors that can prevent the survival of Earth-like life. However, the modern concept of the evolution of the planet assumes the existence more favorable for life climate in the past. If in the past on Mars had formed a biosphere, similar to the one that originated in the early Earth, it is supposed that it is preserved till now in anabiotic state in the bowels of the planet, like microbial communities inhabiting the ancient permafrost of Arctic and Antarctic. In the conditions of modern Martian regolith, this relic life seems to be deprived of the possibility of damage reparation (or these processes occur on a geological time scale), and ionizing radiation should be considered the main factor inhibiting such anabiotic life. In the present study, we studied soil samples, selected in two different extreme habitats of the Earth: ancient permafrost from the Dry Valleys of Antarctica and Xerosol soil from the mountain desert in Morocco, gamma-irradiated with 40 kGy dose at low pressure (1 Torr) and low temperature (-50 °C). Microbial communities inhabiting these samples showed in situ high resistance to the applied effects, retained high number of viable cells, metabolic activity, and high biodiversity. Based on the results, it is assumed that the putative biosphere could be preserved in the dormant state for at least 500 thousand years and 8 million years in the surface layer of Mars regolith and at 5 m depth, respectively, at the current level of ionizing radiation intensity.
Keywords: Mars; astrobiology; gamma radiation; microbial communities; radioresistance.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
100 kGy gamma-affected microbial communities within the ancient Arctic permafrost under simulated Martian conditions.Extremophiles. 2017 Nov;21(6):1057-1067. doi: 10.1007/s00792-017-0966-7. Epub 2017 Oct 9. Extremophiles. 2017. PMID: 28993922
-
The Responses of the Black Fungus Cryomyces Antarcticus to High Doses of Accelerated Helium Ions Radiation within Martian Regolith Simulants and Their Relevance for Mars.Life (Basel). 2020 Jul 31;10(8):130. doi: 10.3390/life10080130. Life (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32752063 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation of Radiation-Resistant Bacteria from Mars Analog Antarctic Dry Valleys by Preselection, and the Correlation between Radiation and Desiccation Resistance.Astrobiology. 2015 Dec;15(12):1076-90. doi: 10.1089/ast.2014.1278. Astrobiology. 2015. PMID: 26684506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early martian environments: the Antarctic and other terrestrial analogs.Adv Space Res. 1989;9(6):147-53. doi: 10.1016/0273-1177(89)90221-4. Adv Space Res. 1989. PMID: 11537365
-
Paleo-Rock-Hosted Life on Earth and the Search on Mars: A Review and Strategy for Exploration.Astrobiology. 2019 Oct;19(10):1230-1262. doi: 10.1089/ast.2018.1960. Epub 2019 Jun 25. Astrobiology. 2019. PMID: 31237436 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Preservation of glycine coordination compounds under a gamma radiation dose representative of natural mars radioactivity.Sci Rep. 2022 Aug 11;12(1):13677. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-17802-y. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35953504 Free PMC article.
-
Radioactive waste microbiology: predicting microbial survival and activity in changing extreme environments.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2024 Jan 12;48(1):fuae001. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuae001. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2024. PMID: 38216518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Soil bacterial communities of Sahara and Gibson deserts: Physiological and taxonomical characteristics.AIMS Microbiol. 2018 Dec 17;4(4):685-710. doi: 10.3934/microbiol.2018.4.685. eCollection 2018. AIMS Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 31294242 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Radiation Intensity, Mineral Matrix, and Pre-Irradiation on the Bacterial Resistance to Gamma Irradiation under Low Temperature Conditions.Microorganisms. 2021 Jan 19;9(1):198. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9010198. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 33477915 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Komarov IA, Isaev VS. Cryology of Mars and other planets of Solar system. Moscow: Nauchnyi mir (Book in Russian); 2010.
-
- Ingersoll AP. Mars: Occurrence of liquid water. Science. 1970;168:972–973. - PubMed
-
- Rummel JD, Beaty DW, Jones MA, et al. A new analysis of Mars “special regions”: findings of the second MEPAG Special Regions Science Analysis Group (SR-SAG2) Astrobiology. 2014;14:887–968. - PubMed
-
- Westall F, Loizeau D, Foucher F, et al. Habitability on Mars from a microbial point of view. Astrobiology. 2013;13:887–897. - PubMed
-
- Ramirez RM, Craddock RA. The geological and climatological case for a warmer and wetter early Mars. Nat Geosci. 2018;11:230–237.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
