Rivaroxaban treatment of cancer-associated venous thromboembolism: Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center institutional experience
- PMID: 31294321
- PMCID: PMC6611365
- DOI: 10.1002/rth2.12215
Rivaroxaban treatment of cancer-associated venous thromboembolism: Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center institutional experience
Abstract
Background: Low-molecular-weight heparin has been the preferred treatment of cancer-associated thrombosis (CAT); however, emerging data support the use of direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs).
Objectives: The Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Clinical Pathway has served as the institutional guideline for the use of rivaroxaban to treat CAT since 2014. Key elements are to recommend against use of a DOAC in patients with active gastrointestinal (GI) or genitourinary tract lesions, and a prespecified dose reduction in the elderly (75+ years old). We present our institutional experience for treatment of CAT.
Methods: From January 2014 through September 2016, 1072 patients began rivaroxaban treatment for CAT; 91.9% had a solid tumor, 8.1% had hematologic malignancies, and 75% of patients with solid tumors had metastatic disease. All patients with CAT treated with rivaroxaban were included in this analysis, regardless of adherence to the Clinical Pathway.
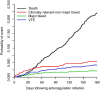
Results: The 6-month cumulative incidence of recurrent venous thromboembolism and major bleeding were 4.2% (95% confidence interval [CI], 2.7%-5.7%) and 2.2% (95% CI, 1.1%-3.2%), respectively. The incidence of clinically relevant non-major bleeding leading to discontinuation of rivaroxaban for at least 7 days was 5.5% (95% CI, 3.7%-7.1%), and 73.3% of major bleeds occurred in the GI tract. The 6-month cumulative mortality rate was 22.2% (95% CI, 19.4%-24.9%). The elderly had similar rates of recurrent thrombosis and bleeding as those aged under 75 years.
Conclusion: Our institutional experience suggests that in appropriately selected patients, rivaroxaban may be used for treatment of CAT with promising safety and efficacy.
Keywords: aged; hemorrhage; neoplasms; rivaroxaban; venous thromboembolism.
Figures
References
-
- Ay C, Pabinger I, Cohen AT. Cancer‐associated venous thromboembolism: burden, mechanisms, and management. Thromb Haemost. 2017;117:219–30. - PubMed
-
- Khorana AA, Francis CW, Culakova E, Kuderer NM, Lyman GH. Thromboembolism is a leading cause of death in cancer patients receiving outpatient chemotherapy. J Thromb Haemost. 2007;5:632–4. - PubMed
-
- Deitcher SR. Cancer‐related deep venous thrombosis: clinical importance, treatment challenges, and management strategies. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2003;29:247–58. - PubMed
-
- Prandoni P. How I treat venous thromboembolism in patients with cancer. Blood. 2005;106:4027–33. - PubMed
-
- Prandoni P, Lensing AW, Piccioli A, Bernardi E, Simioni P, Girolami B, et al. Recurrent venous thromboembolism and bleeding complications during anticoagulant treatment in patients with cancer and venous thrombosis. Blood. 2002;100:3484–363. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

