A free-energy landscape for the glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor GLP1R
- PMID: 31294890
- PMCID: PMC6901726
- DOI: 10.1002/prot.25777
A free-energy landscape for the glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor GLP1R
Abstract
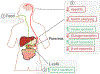
G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are among the most important receptors in human physiology and pathology. They serve as master regulators of numerous key processes and are involved in as well as cause debilitating diseases. Consequently, GPCRs are among the most attractive targets for drug design and pharmaceutical interventions (>30% of drugs on the market). The glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) hormone receptor GLP1R is closely involved in insulin secretion by pancreatic β-cells and constitutes a major druggable target for the development of anti-diabetes and obesity agents. GLP1R structure was recently solved, with ligands, allosteric modulators and as part of a complex with its cognate G protein. However, the translation of this structural data into structure/function understanding remains limited. The current study functionally characterizes GLP1R with special emphasis on ligand and cellular partner binding interactions and presents a free-energy landscape as well as a functional model of the activation cycle of GLP1R. Our results should facilitate a deeper understanding of the molecular mechanism underlying GLP1R activation, forming a basis for improved development of targeted therapeutics for diabetes and related disorders.
Keywords: GLP-1R; GPCR; diabetes; energy-landscape.
© 2019 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

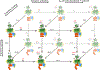
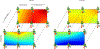
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

