Accurate expression of PD-L1/L2 in lung adenocarcinoma cells: A retrospective study by double immunohistochemistry
- PMID: 31294893
- PMCID: PMC6726681
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.14128
Accurate expression of PD-L1/L2 in lung adenocarcinoma cells: A retrospective study by double immunohistochemistry
Abstract
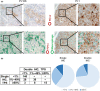
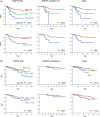
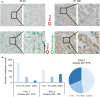
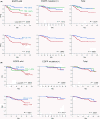
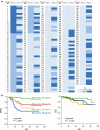
The percentage of programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) positivity in cancer cells, named as the tumor proportion score, is considered to be a predictive biomarker for anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy in lung cancer. PD-L1 is expressed on not only cancer cells but also on immune cells, including macrophages. Although previous studies related to PD-L1/2 expression in cancer tissues have been generally based on single immunohistochemistry (IHC), in the present study, we attempted to evaluate accurate PD-L1/2 expression in cancer cells in lung adenocarcinoma cells using double IHC to also evaluate macrophages. Of the 231 patients, PD-L1 expression was negative in 169 patients (73.2%), 1%-49% positive in 47 patients (20.3%), and ≥50% positive in 15 patients (6.5%). Interestingly, PD-L1 positivity was decreased when using double IHC compared with the estimation by single IHC. High PD-L1 expression was associated with high-grade cancer cells and in higher stage cancer. PD-L2 was negative in 109 patients (47.2%), 1%-49% positive in 50 patients (21.6%), and ≥50% positive in 72 patients (31.2%). The number of PD-L2-positive patients was increased in cases that had an epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation and in lower stage cancer. Thirty-five patients (15.2%) were positive for both PD-L1 and PD-L2, whereas 81 patients (35.1%) were negative for both PD-L1 and PD-L2. Log-rank analysis showed that progression-free survival and overall survival were significantly the longest in the PD-L1-negative and PD-L2-positive groups (P < .0001 and P = .0120). We observed lower PD-L1 or PD-L2 expression in lung adenocarcinoma than previously reported. Double IHC for macrophages may help clinicians to evaluate PD-L1 or PD-L2 expression specifically in cancer cells.
Keywords: PD-L1; PD-L2; lung adenocarcinoma; macrophage; tumor proportion score.
© 2019 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures
References
-
- Poirier AE, Ruan Y, Walter SD, et al. ComPARe Study Team. The future burden of cancer in Canada: long‐term cancer incidence projections 2013‐2042. Cancer Epidemiol. 2019;59:199‐207. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69:7‐34. - PubMed
-
- Fehrenbacher L, Spira A, Ballinger M, et al. Atezolizumab versus docetaxel for patients with previously treated non‐small‐cell lung cancer (POPLAR): a multicentre, open‐label, phase 2 randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2016;387:1837‐1846. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

