RABiT-II-DCA: A Fully-automated Dicentric Chromosome Assay in Multiwell Plates
- PMID: 31295087
- PMCID: PMC8567107
- DOI: 10.1667/RR15266.1
RABiT-II-DCA: A Fully-automated Dicentric Chromosome Assay in Multiwell Plates
Abstract
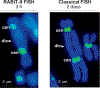
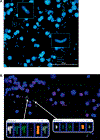
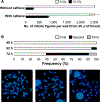
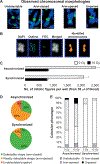
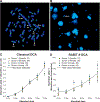
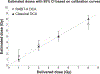
We developed a fully-automated dicentric chromosome assay (DCA) in multiwell plates. All operations, from sample loading to chromosome scoring, are performed, without human intervention, by the second-generation Rapid Automated Biodosimetry Tool II (RABiT-II) robotic system, a plate imager and custom software, FluorQuantDic. The system requires small volumes of blood (30 µl per individual) to determine radiation dose received as a result of a radiation accident or terrorist attack. To visualize dicentrics in multiwell plates, we implemented a non-classical protocol for centromere FISH staining at 37°C. The RABiT-II performs rapid analysis of chromosomes after extracting them from metaphase cells. With the use of multiwell plates, many samples can be screened at the same time. Thus, the RABiT-II DCA provides an advantage during triage when risk-based stratification and medical management are required for a large population exposed to unknown levels of ionizing radiation.
Figures

References
-
- Cytogenetic dosimetry: Applications in preparedness for and response to radiation emergencies. EPR-Biodosimetry 2011; Vienna: International Atomic Energy Agency; 2011.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

