Elucidating Mechanisms of Drug-Resistant Plasmodium falciparum
- PMID: 31295423
- PMCID: PMC6639022
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2019.06.001
Elucidating Mechanisms of Drug-Resistant Plasmodium falciparum
Abstract
Intensified treatment and control efforts since the early 2000s have dramatically reduced the burden of Plasmodium falciparum malaria. However, drug resistance threatens to derail this progress. In this review, we present four antimalarial resistance case studies that differ in timeline, technical approaches, mechanisms of action, and categories of resistance: chloroquine, sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine, artemisinin, and piperaquine. Lessons learned from prior losses of treatment efficacy, drug combinations, and control strategies will help advance mechanistic research into how P. falciparum parasites acquire resistance to current first-line artemisinin-based combination therapies. Understanding resistance in the clinic and laboratory is essential to prolong the effectiveness of current antimalarial drugs and to optimize the pipeline of future medicines.
Keywords: Plasmodium; antimalarials; artemisinin; drug resistance; genetics; genomics; malaria; mutations.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
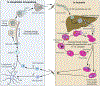
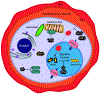
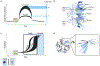
References
-
- Agrawal S, Moser KA, Morton L, Cummings MP, Parihar A, Dwivedi A, Shetty AC, Drabek EF, Jacob CG, Henrich PH, et al. (2017). A novel mutation in the Plasmodium falciparum chloroquine resistance transporter is associated with decreased piperaquine sensitivity. J Infect Dis 216, 468–476. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amato R, Lim P, Miotto O, Amaratunga C, Dek D, Pearson RD, Almagro-Garcia J, Neal AT, Sreng S, Suon S, et al. (2017). Genetic markers associated with dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine failure in Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Cambodia: a genotype-phenotype association study. Lancet Infect Dis 17, 164–173. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

