Inhibitory Activity of Plant Essential Oils against E. coli 1-Deoxy-d-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase
- PMID: 31295807
- PMCID: PMC6681031
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24142518
Inhibitory Activity of Plant Essential Oils against E. coli 1-Deoxy-d-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase
Abstract
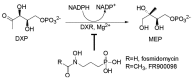
The rate-limiting enzyme of the 2-methyl-d-erythritol-4-phosphate (MEP) terpenoid biosynthetic pathway, 1-deoxy-d-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase (DXR), provides the perfect target for screening new antibacterial substances. In this study, we tested the DXR inhibitory effect of 35 plant essential oils (EOs), which have long been recognized for their antimicrobial properties. The results show that the EOs of Zanbthoxylum bungeanum (ZB), Schizonepetae tenuifoliae (ST), Thymus quinquecostatus (TQ), Origanum vulgare (OV), and Eugenia caryophyllata (EC) displayed weak to medium inhibitory activity against DXR, with IC50 values of 78 μg/mL, 65 μg/mL, 59 μg/mL, 48 μg/mL, and 37 μg/mL, respectively. GC-MS analyses of the above oils and further DXR inhibitory activity tests of their major components revealed that eugenol (EC) and carvacrol (TQ and OV) possess medium inhibition against the protein (68.3% and 55.6%, respectively, at a concentration of 20 μg/mL), whereas thymol (ST, TQ, and OV), carveol (ZB), and linalool (ZB, ST, and OV) only exhibited weak inhibition against DXR, at 20 μg/mL (23%-26%). The results add more details to the antimicrobial mechanisms of plant EOs, which could be very helpful in the direction of the reasonable use of EOs in the food industry and in the control of phytopathogenic microbials.
Keywords: 1-deoxy-d-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase; antibacterial mechanism; inhibition; plant essential oils.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of the manuscript wish to confirm that there are no known conflicts of interest associated with this publication.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antimicrobial mechanism of epigallocatechin gallate and gallocatechin gallate: They target 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase, the key enzyme of the MEP terpenoid biosynthetic pathway.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2017 May 15;622:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2017.04.007. Epub 2017 Apr 18. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2017. PMID: 28428039
-
Antimicrobial mechanism of theaflavins: They target 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase, the key enzyme of the MEP terpenoid biosynthetic pathway.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 12;6:38945. doi: 10.1038/srep38945. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27941853 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of green tea and the catechins against 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase, the key enzyme of the MEP terpenoid biosynthetic pathway.Fitoterapia. 2016 Sep;113:80-4. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2016.07.009. Epub 2016 Jul 18. Fitoterapia. 2016. PMID: 27439219
-
Targeting the methyl erythritol phosphate (MEP) pathway for novel antimalarial, antibacterial and herbicidal drug discovery: inhibition of 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase (DXR) enzyme.Curr Pharm Des. 2007;13(11):1161-77. doi: 10.2174/138161207780618939. Curr Pharm Des. 2007. PMID: 17430177 Review.
-
1-Deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase: an overview.Bioorg Chem. 2004 Dec;32(6):483-93. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2004.08.004. Bioorg Chem. 2004. PMID: 15530989 Review.
Cited by
-
Essential Oil Analysis and Antimicrobial Evaluation of Three Aromatic Plant Species Growing in Saudi Arabia.Molecules. 2021 Feb 11;26(4):959. doi: 10.3390/molecules26040959. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33670315 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive Compounds from Medicinal Plants as Potential Adjuvants in the Treatment of Mild Acne Vulgaris.Molecules. 2024 May 19;29(10):2394. doi: 10.3390/molecules29102394. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38792254 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Molecular Distillation on the Chemical Components, Cleaning, and Antibacterial Abilities of Four Different Citrus Oils.Front Nutr. 2021 Sep 1;8:731724. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.731724. eCollection 2021. Front Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34540881 Free PMC article.
-
The Chemical Composition and Biological Activities of Essential Oil from Korean Native Thyme Bak-Ri-Hyang (Thymus quinquecostatus Celak.).Molecules. 2022 Jul 1;27(13):4251. doi: 10.3390/molecules27134251. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35807496 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hammer K.A., Carson C.F. Antibacterial and antifungal activities of EOs. In: Thormar H., editor. Lipids and EOs as Antimicrobial Agents. Wiley; Huboken, NJ, USA: 2011. pp. 255–306.
-
- Al-Sayed E. Unearthing the chemical composition of Taxodium distichum (L.) Rich. leaf essential oil and its antimicrobial activity. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018;126:76–82. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.10.009. - DOI
-
- Knezevic P., Aleksic V., Simin N., Svircev E., Petrovic A., Mimica-Dukic N. Antimicrobialactivity of Eucalyptus camaldulensis essential oils and their interactions with conventional antimicrobial agents against multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016;178:125–136. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.12.008. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

