Visual Analog Scale Ratings and Orthographic Transcription Measures of Sentence Intelligibility in Parkinson's Disease With Variable Listener Exposure
- PMID: 31296027
- PMCID: PMC6802923
- DOI: 10.1044/2019_AJSLP-18-0275
Visual Analog Scale Ratings and Orthographic Transcription Measures of Sentence Intelligibility in Parkinson's Disease With Variable Listener Exposure
Abstract
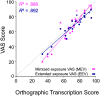
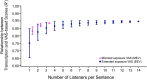
Purpose While orthographic transcription (OT) is the gold standard for measures of intelligibility, it is relatively inaccessible to clinicians. This study investigates the relationship between visual analog scale (VAS) ratings and OT measures of intelligibility for speakers with Parkinson's disease (PD), with the eventual goal of developing more clinically feasible assessments of intelligibility. Method Twenty speakers with PD and 5 controls read 11 sentences. First, 33 listeners completed an OT task using 1 sentence from each speaker. An additional 33 listeners rated the intelligibility of 1 sentence from each speaker using a VAS, reflecting a minimized exposure VAS (MEV) task. Lastly, 14 additional listeners each rated the intelligibility of all 11 sentences produced by all speakers using a VAS, reflecting an extended exposure VAS (EEV) task. Smaller listener groups were simulated from each VAS task for comparison to scores from the OT task. Results There was a strong relationship between OT and both MEV and EEV. This relationship remained strong (R 2 ≥ .82) even when only 1 listener in MEV and 2 listeners in EEV were simulated per sentence. Conclusions VAS ratings may be a suitable alternative to OT measures of sentence intelligibility for PD using listeners with both minimal and extended exposure to the stimuli.
Figures


References
-
- Adams S. G., Dykstra A., Jenkins M., & Jog M. (2008). Speech-to-noise levels and conversational intelligibility in hypophonia and Parkinson's disease. Journal of Medical Speech-Language Pathology, 16(4), 165–173.
-
- American Speech-Language-Hearing Association. (2005). Guidelines for manual pure-tone threshold audiometry. Rockville, MD: Author.
-
- Beukelman D. R., & Yorkston K. M. (1980). Influence of passage familiarity on intelligibility estimates of dysarthric speech. Journal of Communication Disorders, 13(1), 33–41. - PubMed
-
- Cannito M. P., Suiter D. M., Beverly D., Chorna L., Wolf T., & Pfeiffer R. M. (2012). Sentence intelligibility before and after voice treatment in speakers with idiopathic Parkinson's disease. Journal of Voice, 26(2), 214–219. - PubMed
-
- DePaul R., & Kent R. D. (2000). A longitudinal case study of ALS: Effects of listener familiarity and proficiency on intelligibility judgments. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 9(3), 230–240.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

