Noninvasive In Vivo Quantification of Adeno-Associated Virus Serotype 9-Mediated Expression of the Sodium/Iodide Symporter Under Hindlimb Ischemia and Neuraminidase Desialylation in Skeletal Muscle Using Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography/Computed Tomography
- PMID: 31296047
- PMCID: PMC6629470
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.119.009063
Noninvasive In Vivo Quantification of Adeno-Associated Virus Serotype 9-Mediated Expression of the Sodium/Iodide Symporter Under Hindlimb Ischemia and Neuraminidase Desialylation in Skeletal Muscle Using Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography/Computed Tomography
Abstract
Background: We propose micro single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography imaging of the hNIS (human sodium/iodide symporter) to noninvasively quantify adeno-associated virus 9 (AAV9)-mediated gene expression in a murine model of peripheral artery disease.
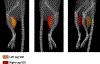
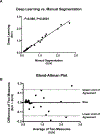
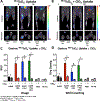
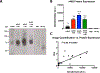
Methods: AAV9-hNIS (2×1011 viral genome particles) was injected into nonischemic or ischemic gastrocnemius muscles of C57Bl/6J mice following unilateral hindlimb ischemia ± the α-sialidase NA (neuraminidase). Control nonischemic limbs were injected with phosphate buffered saline or remained noninjected. Twelve mice underwent micro single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography imaging after serial injection of pertechnetate (99mTcO4-), a NIS substrate, up to 28 days after AAV9-hNIS injection. Twenty four animals were euthanized at selected times over 1 month for ex vivo validation. Forty-two animals were imaged with 99mTcO4- ± the selective NIS inhibitor perchlorate on day 10, to ascertain specificity of radiotracer uptake. Tissue was harvested for ex vivo validation. A modified version of the U-Net deep learning algorithm was used for image quantification.
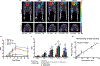
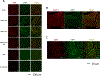
Results: As quantitated by standardized uptake value, there was a gradual temporal increase in 99mTcO4- uptake in muscles treated with AAV9-hNIS. Hindlimb ischemia, NA, and hindlimb ischemia plus NA increased the magnitude of 99mTcO4- uptake by 4- to 5-fold compared with nonischemic muscle treated with only AAV9-hNIS. Perchlorate treatment significantly reduced 99mTcO4- uptake in AAV9-hNIS-treated muscles, demonstrating uptake specificity. The imaging results correlated well with ex vivo well counting (r2=0.9375; P<0.0001) and immunoblot analysis of NIS protein (r2=0.65; P<0.0001).
Conclusions: Micro single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography imaging of hNIS-mediated 99mTcO4- uptake allows for accurate in vivo quantification of AAV9-driven gene expression, which increases under ischemic conditions or neuraminidase desialylation in skeletal muscle.
Keywords: animals; genetic therapy; neuraminidase; peripheral artery disease; tomography, emission computed, single-photon.
Figures

Comment in
-
New Tricks for an Aging Dog.Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019 Jul;12(7):e009452. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.119.009452. Epub 2019 Jul 12. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019. PMID: 31296046 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ouriel K Peripheral arterial disease. The Lancet. 2001;358:1257–1264 - PubMed
-
- Ghosh R, Walsh S, Tang T, Noorani A, Hayes P. Gene therapy as a novel therapeutic option in the treatment of peripheral vascular disease: Systematic review and meta‐analysis. Int J Clin Pract. 2008;62:1383–1390 - PubMed
-
- Jones WS, Annex BH. Growth factors for therapeutic angiogenesis in peripheral arterial disease. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2007;22:458–463 - PubMed
-
- Boden J, Lassance-Soares RM, Wang H, Wei Y, Spiga MG, Adi J, Layman H, Yu H, Vazquez-Padron RI, Andreopoulos F, Webster KA. Vascular regeneration in ischemic hindlimb by adeno-associated virus expressing conditionally silenced vascular endothelial growth factor. J Am Heart Assoc.2016;5:1–19. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

