Angiographic assessment of the efficacy of flow diverter treatment for cerebral aneurysms
- PMID: 31296064
- PMCID: PMC6838848
- DOI: 10.1177/1591019919860829
Angiographic assessment of the efficacy of flow diverter treatment for cerebral aneurysms
Abstract
Background: The recent growth of neuro-endovascular treatment has rekindled interest in the use of angiographic techniques for flow assessment. Aneurysm treatment with flow diverters is particularly amenable to such analysis. We analyze contrast time-density curves - recorded within aneurysms before (pre) and immediately after (post) flow diverter implantation to estimate six-month treatment outcomes.
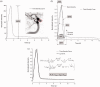
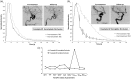
Methods: Fifty-six patients with 65 aneurysms were treated with flow diverters at two institutions. A region of interest was drawn around the aneurysm perimeter in image sequences taken both pre and post angiography, and the temporal variation in grayscale intensity within the aneurysm (time-density curve) was recorded. Eleven parameters were quantified from each time-density curve. Aneurysm occlusion status was recorded six months post treatment. The change in parameters from pre to post treatment was statistically evaluated between aneurysm occluded and non-occluded groups.
Results: Of the 11 parameters, eight were significantly different before and immediately after flow diversion. Considering the entire data set, none of the parameters was statistically different between the occluded and non-occluded groups. However, subgroup analyses showed that four variables were significantly different between the aneurysm occluded and non-occluded groups. The sensitivity of these variables to predict aneurysm occlusion at six months ranged from 60% to 89%, while the specificity ranged from 55% to 70%.
Conclusions: Device-induced intra-aneurysmal flow alterations quantified by simple aneurysmal time-density curves can potentially be used to predict long-term outcomes of flow diversion. Large multi-center studies will be required to confirm these findings. Patient-to-patient variability in coagulation may need to be incorporated for clinically relevant predictive values.
Keywords: Concentration–time curve; contrast washout; time–density curve.
Figures


References
-
- Lieber BB, Sadasivan C, Gounis MJ, et al. Functional angiography. Crit Rev Biomed Eng 2005; 33: 1–102. - PubMed
-
- Shpilfoygel SD, Close RA, Valentino DJ, et al. X-ray videodensitometric methods for blood flow and velocity measurement: a critical review of literature. Med Phys 2000; 27: 2008–2023. - PubMed
-
- Hilal SK. Determination of the blood flow by a radiographic technique. Physical considerations and experimental results. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med 1966; 96: 896–906. - PubMed
-
- Kovarovic B, Woo HH, Fiorella D, et al. Pressure and flow rate changes during contrast injections in cerebral angiography: correlation to reflux length. Cardiovasc Eng Technol 2018; 9: 226–239. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

