Comparison of risk of stroke in patients treated with peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 31296101
- PMCID: PMC6691832
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2019.1632210
Comparison of risk of stroke in patients treated with peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
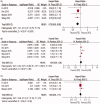
Objective: Accumulating evidence has demonstrated that dialysis patients are at increased risk for stroke. However, the impact of dialysis modalities on stroke risk remains controversial. We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to determine the effect of peritoneal dialysis (PD) and hemodialysis (HD) on stroke risk. Methods: A systematic search of PubMed, EMBASE, and Web of Science was performed to identify articles comparing the stroke outcomes of dialysis patients. Hazard ratios (HRs) with 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs) were extracted and synthesized to examine stroke outcomes, including ischemic stroke, hemorrhagic stroke, and overall stroke. Results: The search yielded five studies composed of 1,219,245 patients that were evaluated in the final analysis. The results showed that PD was associated with a lower risk for hemorrhagic stroke compared with HD (HR = 0.78; 95% CI: 0.69-0.88; p < 0.001). For ischemic stroke, the results showed that PD was associated with a higher risk compared with HD among the non-Asian patients (HR = 1.13; 95% CI: 1.05-1.23; p = 0.002), but there were no significant differences between PD and HD for the Asian patients. Similarly, there were no significant differences between the effects of the PD and HD approaches on overall stroke risk. Conclusions: We observed that PD patients were less likely to develop hemorrhagic stroke than HD patients, and the risk for ischemic stroke was significantly higher for PD patients than for HD patients among the non-Asian patients. However, our findings could be biased due to the heterogeneity of the included studies.
Keywords: Peritoneal dialysis; hemodialysis; meta-analysis; stroke.
Figures

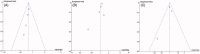
References
-
- Karopadi AN, Mason G, Rettore E, et al. . The role of economies of scale in the cost of dialysis across the world: a macroeconomic perspective. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2014;29:885–892. - PubMed
-
- Kim H, Kim KH, Ahn SV, et al. . Risk of major cardiovascular events among incident dialysis patients: a Korean national population-based study. Int J Cardiol. 2015;198:95–101. - PubMed
-
- Wang HH, Hung SY, Sung JM, et al. . Risk of stroke in long-term dialysis patients compared with the general population. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014;63:604–611. - PubMed
-
- Zoccali C, Mallamaci F, Tripepi G. Traditional and emerging cardiovascular risk factors in end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int Suppl. 2003; 63:S105–S110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
