Associations Between Reproductive Coercion, Partner Violence, and Mental Health Symptoms Among Young Black Women in Baltimore, Maryland
- PMID: 31296104
- PMCID: PMC6954344
- DOI: 10.1177/0886260519860900
Associations Between Reproductive Coercion, Partner Violence, and Mental Health Symptoms Among Young Black Women in Baltimore, Maryland
Abstract
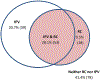
This study examined the associations of reproductive coercion (RC) with mental health of Black adolescent and young adult women. We tested RC as a predictor of depression and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms. We also explored the interaction of exposure to RC and physical and sexual intimate partner violence (IPV) as they relate to depression and PTSD symptoms. A primarily community-based convenience sample of 188 self-identified Black women, aged 18 to 25 years, in Baltimore, Maryland, completed computer-based cross-sectional surveys. Lifetime RC (37.8%) and IPV (48.9%) were prevalent in this sample. Nearly 10% of the young women reported experiencing RC without IPV; 38% of the sample reported experiencing both types of violence. Depression (69%) and PTSD (47.1%) symptoms were more prevalent among women with RC than among women without RC. Adjusted results revealed RC and IPV were independently associated with depression (adjusted odds ratioRC = 2.86, 95% CI = [1.38, 5.94] and adjusted odds ratioIPV = 5.15, 95% CI = [2.47, 10.76]). Similarly, RC and IPV were independently associated with PTSD (adjusted odds ratioRC = 2.41, 95% CI = [1.15, 5.08] and adjusted odds ratioIPV = 3.04, 95% CI = [1.39, 6.63]). Findings suggest that RC and IPV independently contribute to mental health morbidities among this population of women. Current policies in health care practice increasingly recommend provision of screening for IPV, including RC. These practices should extend to women receiving services in community-based settings, thus strengthening the linkage to referral for further mental health treatment and victim service support. In the context of the social burdens affecting young Black women's health, a comprehensive approach that integrates mental health and reproductive/sexual health care is essential for women reporting RC experiences.
Keywords: depression; domestic violence; intimate partner violence; post-traumatic stress disorder; reproductive coercion.
Figures
References
-
- Afifi TO, Macmillan H, Cox BJ, Asmundson GJG, Stein MB, & Sareen J (2009). Mental Health Correlates of Intimate Partner Violence in Marital Relationships in a Nationally Representative Sample of Males and Females. Journal of Interpersonal Violence, 24, 1398–1417. 10.1177/0886260508322192 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alexander KA, Volpe EM, Abboud S, & Campbell JC (2016). Reproductive coercion, sexual risk behaviours and mental health symptoms among young low-income behaviourally bisexual women: implications for nursing practice. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 25, 3533–3544. 10.1111/jocn.13238 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical