The evolutionary history of LysM-RLKs (LYKs/LYRs) in wild tomatoes
- PMID: 31296160
- PMCID: PMC6625017
- DOI: 10.1186/s12862-019-1467-3
The evolutionary history of LysM-RLKs (LYKs/LYRs) in wild tomatoes
Abstract
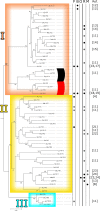
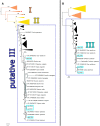
Background: The LysM receptor-like kinases (LysM-RLKs) are important to both plant defense and symbiosis. Previous studies described three clades of LysM-RLKs: LysM-I/LYKs (10+ exons per gene and containing conserved kinase residues), LysM-II/LYRs (1-5 exons per gene, lacking conserved kinase residues), and LysM-III (two exons per gene, with a kinase unlike other LysM-RLK kinases and restricted to legumes). LysM-II gene products are presumably not functional as conventional receptor kinases, but several are known to operate in complexes with other LysM-RLKs. One aim of our study was to take advantage of recently mapped wild tomato transcriptomes to evaluate the evolutionary history of LysM-RLKs within and between species. The second aim was to place these results into a broader phylogenetic context by integrating them into a sequence analysis of LysM-RLKs from other functionally well-characterized model plant species. Furthermore, we sought to assess whether the Group III LysM-RLKs were restricted to the legumes or found more broadly across Angiosperms.
Results: Purifying selection was found to be the prevailing form of natural selection within species at LysM-RLKs. No signatures of balancing selection were found in species-wide samples of two wild tomato species. Most genes showed a greater extent of purifying selection in their intracellular domains, with the exception of SlLYK3 which showed strong purifying selection in both the extracellular and intracellular domains in wild tomato species. The phylogenetic analysis did not reveal a clustering of microbe/functional specificity to groups of closely related proteins. We also discovered new putative LysM-III genes in a range of Rosid species, including Eucalyptus grandis.
Conclusions: The LysM-III genes likely originated before the divergence of E. grandis from other Rosids via a fusion of a Group II LysM triplet and a kinase from another RLK family. SlLYK3 emerges as an especially interesting candidate for further study due to the high protein sequence conservation within species, its position in a clade of LysM-RLKs with distinct LysM domains, and its close evolutionary relationship with LYK3 from Arabidopsis thaliana.
Keywords: Phylogenetics; Plant immunity; Population genetics; Solanum; Symbiosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Laura E. Rose is a member of the editorial board (Associate Editor) of this journal.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A New Classification of Lysin Motif Receptor-Like Kinases in Lotus japonicus.Plant Cell Physiol. 2023 Mar 1;64(2):176-190. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcac156. Plant Cell Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36334262
-
The tomato RLK superfamily: phylogeny and functional predictions about the role of the LRRII-RLK subfamily in antiviral defense.BMC Plant Biol. 2012 Dec 2;12:229. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-12-229. BMC Plant Biol. 2012. PMID: 23198823 Free PMC article.
-
Analyses of Lysin-motif Receptor-like Kinase (LysM-RLK) Gene Family in Allotetraploid Brassica napus L. and Its Progenitor Species: An In Silico Study.Cells. 2021 Dec 23;11(1):37. doi: 10.3390/cells11010037. Cells. 2021. PMID: 35011598 Free PMC article.
-
Knowing your friends and foes--plant receptor-like kinases as initiators of symbiosis or defence.New Phytol. 2014 Dec;204(4):791-802. doi: 10.1111/nph.13117. New Phytol. 2014. PMID: 25367611 Review.
-
LysM Receptor-Like Kinase and LysM Receptor-Like Protein Families: An Update on Phylogeny and Functional Characterization.Front Plant Sci. 2018 Oct 24;9:1531. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01531. eCollection 2018. Front Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 30405668 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide identification of lysin motif containing protein family genes in eight rosaceae species, and expression analysis in response to pathogenic fungus Botryosphaeria dothidea in Chinese white pear.BMC Genomics. 2020 Sep 7;21(1):612. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-07032-9. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32894061 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of LysM gene family members and their expression in response to Colletotrichum fructicola infection in Octoploid strawberry(Fragaria × ananassa).Front Plant Sci. 2023 Jan 23;13:1105591. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1105591. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 36756233 Free PMC article.
-
Lysin Motif (LysM) Proteins: Interlinking Manipulation of Plant Immunity and Fungi.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 18;22(6):3114. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063114. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33803725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toward Understanding the Molecular Recognition of Fungal Chitin and Activation of the Plant Defense Mechanism in Horticultural Crops.Molecules. 2021 Oct 28;26(21):6513. doi: 10.3390/molecules26216513. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34770922 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

