Transcriptome analysis reveals candidate genes related to phosphorus starvation tolerance in sorghum
- PMID: 31296169
- PMCID: PMC6624980
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-019-1914-8
Transcriptome analysis reveals candidate genes related to phosphorus starvation tolerance in sorghum
Abstract
Background: Phosphorus (P) deficiency in soil is a worldwide issue and a major constraint on the production of sorghum, which is an important staple food, forage and energy crop. The depletion of P reserves and the increasing price of P fertilizer make fertilizer application impractical, especially in developing countries. Therefore, identifying sorghum accessions with low-P tolerance and understanding the underlying molecular basis for this tolerance will facilitate the breeding of P-efficient plants, thereby resolving the P crisis in sorghum farming. However, knowledge in these areas is very limited.
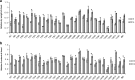
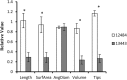
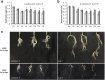
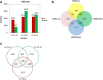
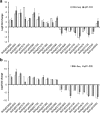
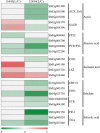
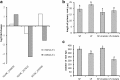
Results: The 29 sorghum accessions used in this study demonstrated great variability in their tolerance to low-P stress. The internal P content in the shoot was correlated with P tolerance. A low-P-tolerant accession and a low-P-sensitive accession were chosen for RNA-seq analysis to identify potential underlying molecular mechanisms. A total of 2089 candidate genes related to P starvation tolerance were revealed and found to be enriched in 11 pathways. Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analyses showed that the candidate genes were associated with oxidoreductase activity. In addition, further study showed that malate affected the length of the primary root and the number of tips in sorghum suffering from low-P stress.
Conclusions: Our results show that acquisition of P from soil contributes to low-P tolerance in different sorghum accessions; however, the underlying molecular mechanism is complicated. Plant hormone (including auxin, ethylene, jasmonic acid, salicylic acid and abscisic acid) signal transduction related genes and many transcriptional factors were found to be involved in low-P tolerance in sorghum. The identified accessions will be useful for breeding new sorghum varieties with enhanced P starvation tolerance.
Keywords: Candidate genes; Malate; Phosphorus starvation; Root development; Sorghum; Transcriptome analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization of contrasting rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes reveals the Pi-efficient schema for phosphate starvation tolerance.BMC Plant Biol. 2021 Jun 21;21(1):282. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-03015-4. BMC Plant Biol. 2021. PMID: 34154533 Free PMC article.
-
The genetic architecture of phosphorus efficiency in sorghum involves pleiotropic QTL for root morphology and grain yield under low phosphorus availability in the soil.BMC Plant Biol. 2019 Feb 28;19(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-1689-y. BMC Plant Biol. 2019. PMID: 30819116 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Key Genes Regulating Sorghum Mesocotyl Elongation through Transcriptome Analysis.Genes (Basel). 2023 Jun 2;14(6):1215. doi: 10.3390/genes14061215. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37372395 Free PMC article.
-
Drought and High Temperature Stress in Sorghum: Physiological, Genetic, and Molecular Insights and Breeding Approaches.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 11;22(18):9826. doi: 10.3390/ijms22189826. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34575989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress of Research on the Physiology and Molecular Regulation of Sorghum Growth under Salt Stress by Gibberellin.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 5;24(7):6777. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076777. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047750 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Systematic Identification and Expression Analysis of the Sorghum Pht1 Gene Family Reveals Several New Members Encoding High-Affinity Phosphate Transporters.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 10;23(22):13855. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213855. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430345 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome Changes Induced by Different Potassium Levels in Banana Roots.Plants (Basel). 2019 Dec 19;9(1):11. doi: 10.3390/plants9010011. Plants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31861661 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of contrasting rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes reveals the Pi-efficient schema for phosphate starvation tolerance.BMC Plant Biol. 2021 Jun 21;21(1):282. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-03015-4. BMC Plant Biol. 2021. PMID: 34154533 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis of Pennisetum americanum × Pennisetum purpureum and Pennisetum americanum leaves in response to high-phosphorus stress.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Jul 6;24(1):635. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05339-3. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 38971717 Free PMC article.
-
Response of Soybean Root to Phosphorus Deficiency under Sucrose Feeding: Insight from Morphological and Metabolome Characterizations.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Aug 21;2020:2148032. doi: 10.1155/2020/2148032. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32904516 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marschner H, Rimmington G. Mineral nutrition of higher plants. Plant Cell Environ. 1988;11:147–148.
-
- Raghothama KG, Karthikeyan AS. Phosphate acquisition. Plant Soil. 2005;274:37–49. doi: 10.1007/s11104-004-2005-6. - DOI
-
- Holford ICR. Soil phosphorus: its measurement, and its uptake by plants. Soil Res. 1997;35:227–240. doi: 10.1071/S96047. - DOI
-
- Hinsinger P. Bioavailability of soil inorganic P in the rhizosphere as affected by root-induced chemical changes: a review. Plant Soil. 2001;237:173–195. doi: 10.1023/A:1013351617532. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

