Pineal gland dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease: relationship with the immune-pineal axis, sleep disturbance, and neurogenesis
- PMID: 31296240
- PMCID: PMC6624939
- DOI: 10.1186/s13024-019-0330-8
Pineal gland dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease: relationship with the immune-pineal axis, sleep disturbance, and neurogenesis
Abstract
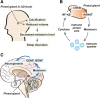
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a globally common neurodegenerative disease, which is accompanied by alterations to various lifestyle patterns, such as sleep disturbance. The pineal gland is the primary endocrine organ that secretes hormones, such as melatonin, and controls the circadian rhythms. The decrease in pineal gland volume and pineal calcification leads to the reduction of melatonin production. Melatonin has been reported to have multiple roles in the central nervous system (CNS), including improving neurogenesis and synaptic plasticity, suppressing neuroinflammation, enhancing memory function, and protecting against oxidative stress. Recently, reduced pineal gland volume and pineal calcification, accompanied by cognitive decline and sleep disturbances have been observed in AD patients. Here, I review current significant evidence of the contribution of pineal dysfunction in AD to the progress of AD neuropathology. I suggest new insights to understanding the relationship between AD pathogenesis and pineal gland function.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease (AD); Circadian rhythms; Immune-pineal axis; Melatonin; Pineal calcification; Pineal gland.
Conflict of interest statement
The author has no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The human pineal gland and melatonin in aging and Alzheimer's disease.J Pineal Res. 2005 Apr;38(3):145-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2004.00196.x. J Pineal Res. 2005. PMID: 15725334 Review.
-
Disturbance and strategies for reactivation of the circadian rhythm system in aging and Alzheimer's disease.Sleep Med. 2007 Sep;8(6):623-36. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2006.11.010. Epub 2007 Mar 26. Sleep Med. 2007. PMID: 17383938 Review.
-
Melatonin in Alzheimer's Disease: A Latent Endogenous Regulator of Neurogenesis to Mitigate Alzheimer's Neuropathology.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Dec;56(12):8255-8276. doi: 10.1007/s12035-019-01660-3. Epub 2019 Jun 17. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 31209782 Review.
-
Pineal clock gene oscillation is disturbed in Alzheimer's disease, due to functional disconnection from the "master clock".FASEB J. 2006 Sep;20(11):1874-6. doi: 10.1096/fj.05-4446fje. Epub 2006 Jul 3. FASEB J. 2006. PMID: 16818472
-
Melatonin as a Harmonizing Factor of Circadian Rhythms, Neuronal Cell Cycle and Neurogenesis: Additional Arguments for Its Therapeutic Use in Alzheimer's Disease.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2023;21(5):1273-1298. doi: 10.2174/1570159X21666230314142505. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36918783 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Quantitative imaging of natural products in fine brain regions using desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry imaging (DESI-MSI): Uncaria alkaloids as a case study.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2022 Jul;414(17):4999-5007. doi: 10.1007/s00216-022-04130-3. Epub 2022 May 31. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2022. PMID: 35639139
-
[Gandou Bushen Decoction Ameliorates Cognitive Impairment in Wilson Disease Model TX Mice by Regulating Melatonin Synthesis via the SIRT3/FOXO3α Pathway].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025 Jan 20;56(1):102-111. doi: 10.12182/20250160602. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025. PMID: 40109448 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Role of Melatonin in the Management of Sleep and Circadian Disorders in the Context of Psychiatric Illness.Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2022 Nov;24(11):623-634. doi: 10.1007/s11920-022-01369-6. Epub 2022 Oct 13. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2022. PMID: 36227449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Melatonin: A Potential Candidate for the Treatment of Experimental and Clinical Perinatal Asphyxia.Molecules. 2023 Jan 22;28(3):1105. doi: 10.3390/molecules28031105. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36770769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Melatonin Reduces Neuroinflammation and Improves Axonal Hypomyelination by Modulating M1/M2 Microglia Polarization via JAK2-STAT3-Telomerase Pathway in Postnatal Rats Exposed to Lipopolysaccharide.Mol Neurobiol. 2021 Dec;58(12):6552-6576. doi: 10.1007/s12035-021-02568-7. Epub 2021 Sep 28. Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 34585328 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

