Immunomodulatory effects of Rhipicephalus haemaphysaloides serpin RHS2 on host immune responses
- PMID: 31296257
- PMCID: PMC6624921
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-019-3607-4
Immunomodulatory effects of Rhipicephalus haemaphysaloides serpin RHS2 on host immune responses
Abstract
Background: Rhipicephalus haemaphysaloides is a widespread tick species in China and other South East Asian countries, where it is the vector of many pathogens. The objective of this study was to study the role of serpin (serine protease inhibitor) during the tick-host interaction.
Methods: The differentiation of bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (BMDC) was induced in vitro, and the effect of RHS2 on the maturation of DCs was evaluated. The effects of RHS2 on T cell activation and cytotoxic T lymphocytes' (CTLs) activity were analyzed by flow cytometry. Antibody subtypes after immunization of mice with RHS2 and OVA were determined.
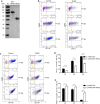
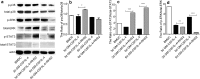
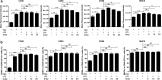
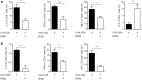
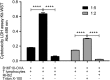
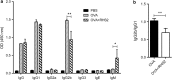
Results: RHS2 can inhibit the differentiation of bone marrow-derived cells into DCs and promote their differentiation into macrophages. RHS2 can inhibit the maturation of DCs and the expression of CD80, CD86 and MHCII. The number of CD3+CD4+ and CD3+CD8+ T cells secreting IFN-γ, IL-2 and TNF-α was decreased, and the number of CD3+CD4+ T cells secreting IL-4 was increased, indicating that RHS2 can inhibit the activation of CD4 T cells and CD8 T cells, leading to inhibition of Th1 immune response. RHS2 inhibits the elimination of target cells by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. After immunization of mice with RHS2 and OVA, serum IgG2b was significantly reduced and IgM was increased.
Conclusions: The results show that RHS2 has an inhibitory effect on the host immune response. Ticks have evolved various ways to circumvent adaptive immunity. Their serpin inhibits BMDC differentiation to reduce immune responses.
Keywords: BMDC; Immmunomodulatory; Rhipicephalus haemaphysaloides; Serpin; Tick.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A family of serine protease inhibitors (serpins) and its expression profiles in the ovaries of Rhipicephalus haemaphysaloides.Infect Genet Evol. 2020 Oct;84:104346. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2020.104346. Epub 2020 Apr 29. Infect Genet Evol. 2020. PMID: 32360539
-
Interaction between saliva's adenosine and tick parasitism: effects on feeding and reproduction.Parasit Vectors. 2017 Jul 10;10(1):326. doi: 10.1186/s13071-017-2248-8. Parasit Vectors. 2017. PMID: 28693553 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypic profile of dendritic and T cells in the lymph node of Balb/C mice with breast cancer submitted to dendritic cells immunotherapy.Immunol Lett. 2016 Sep;177:25-37. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2016.07.009. Epub 2016 Jul 14. Immunol Lett. 2016. PMID: 27423825
-
Tick saliva inhibits the chemotactic function of MIP-1alpha and selectively impairs chemotaxis of immature dendritic cells by down-regulating cell-surface CCR5.Int J Parasitol. 2008 May;38(6):705-16. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2007.10.006. Epub 2007 Oct 22. Int J Parasitol. 2008. PMID: 18023445
-
Splenic dendritic cells pulsed with Ixodes ricinus tick saliva prime naive CD4+T to induce Th2 cell differentiation in vitro and in vivo.Int Immunol. 2007 Apr;19(4):535-43. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxm019. Epub 2007 Mar 6. Int Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17344202
Cited by
-
The α-Gal epitope - the cause of a global allergic disease.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 22;15:1335911. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1335911. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38318181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-Wide Characterization and Comparative Genomic Analysis of the Serpin Gene Family in Microsporidian Nosema bombycis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 29;24(1):550. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010550. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613990 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Phylogenetic Analysis of the Serpin Superfamily.Mol Biol Evol. 2021 Jun 25;38(7):2915-2929. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msab081. Mol Biol Evol. 2021. PMID: 33744972 Free PMC article.
-
Serpins in Tick Physiology and Tick-Host Interaction.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 May 19;12:892770. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.892770. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35711658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Key molecules regulating the blood meals of Rhipicephalus sanguineus (Acari: Ixodidae) revealed by transcriptomics.Vet Res Forum. 2024;15(4):171-179. doi: 10.30466/vrf.2024.2011271.4007. Epub 2024 Apr 15. Vet Res Forum. 2024. PMID: 38770198 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

