A cytosine deaminase for programmable single-base RNA editing
- PMID: 31296651
- PMCID: PMC6956565
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aax7063
A cytosine deaminase for programmable single-base RNA editing
Abstract
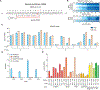
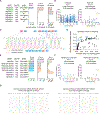
Programmable RNA editing enables reversible recoding of RNA information for research and disease treatment. Previously, we developed a programmable adenosine-to-inosine (A-to-I) RNA editing approach by fusing catalytically inactivate RNA-targeting CRISPR-Cas13 (dCas13) with the adenine deaminase domain of ADAR2. Here, we report a cytidine-to-uridine (C-to-U) RNA editor, referred to as RNA Editing for Specific C-to-U Exchange (RESCUE), by directly evolving ADAR2 into a cytidine deaminase. RESCUE doubles the number of mutations targetable by RNA editing and enables modulation of phosphosignaling-relevant residues. We apply RESCUE to drive β-catenin activation and cellular growth. Furthermore, RESCUE retains A-to-I editing activity, enabling multiplexed C-to-U and A-to-I editing through the use of tailored guide RNAs.
Copyright © 2019, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Comment in
-
Expanding options for RNA based editors.Nat Rev Genet. 2019 Oct;20(10):563. doi: 10.1038/s41576-019-0167-6. Nat Rev Genet. 2019. PMID: 31388142 No abstract available.
References
-
- Cassidy-Amstutz C et al. , Identification of a Minimal Peptide Tag for in Vivo and in Vitro Loading of Encapsulin. Biochemistry 55, 3461–3468 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

