CeO2NPs relieve radiofrequency radiation, improve testosterone synthesis, and clock gene expression in Leydig cells by enhancing antioxidation
- PMID: 31296989
- PMCID: PMC6598754
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S206561
CeO2NPs relieve radiofrequency radiation, improve testosterone synthesis, and clock gene expression in Leydig cells by enhancing antioxidation
Abstract
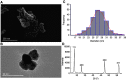
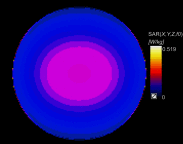
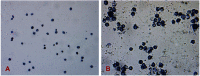
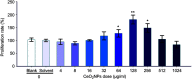
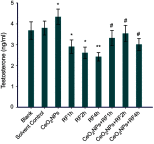
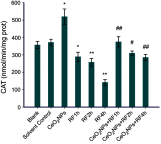
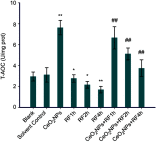
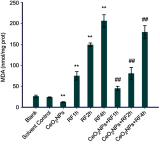
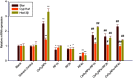
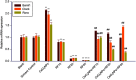
Introduction: The ratio of Ce3+/Ce4+ in their structure confers unique functions on cerium oxide nanoparticles (CeO2NPs) containing rare earth elements in scavenging free radicals and protecting against oxidative damage. The potential of CeO2NPs to protect testosterone synthesis in primary mouse Leydig cells during exposure to 1,800 MHz radiofrequency (RF) radiation was examined in vitro. Methods: Leydig cells were treated with different concentrations of CeO2NPs to identify the optimum concentration for cell proliferation. The cells were pretreated with the optimum dose of CeO2NPs for 24 hrs and then exposed to 1,800 MHz RF at a power density of 200.27 µW/cm2 (specific absorption rate (SAR), 0.116 W/kg) for 1 hr, 2 hrs, or 4 hrs. The medium was used to measure the testosterone concentration. The cells were collected to determine the antioxidant indices (catalase [CAT], malondialdehyde [MDA], and total antioxidant capacity [T-AOC]), and the mRNA expression of the testosterone synthase genes (Star, Cyp11a1, and Hsd-3β) and clock genes (Clock, Bmal1, and Rorα). Results: Our preliminary result showed that 128 μg/mL CeO2NPs was the optimum dose for cell proliferation. Cells exposed to RF alone showed reduced levels of testosterone, T-AOC, and CAT activities, increased MDA content, and the downregulated genes expression of Star, Cyp11a1, Hsd-3β, Clock, Bmal1, and Rorα. Pretreatment of the cells with 128 μg/mL CeO2NPs for 24 hrs followed by RF exposure significantly increased testosterone synthesis, upregulated the expression of the testosterone synthase and clock genes, and increased the resistance to oxidative damage in Leydig cells compared with those in cells exposed to RF alone. Conclusion: Exposure to 1,800 MHz RF had adverse effects on testosterone synthesis, antioxidant levels, and clock gene expression in primary Leydig cells. Pretreatment with CeO2NPs prevented the adverse effects on testosterone synthesis induced by RF exposure by regulating their antioxidant capacity and clock gene expression in vitro. Further studies of the mechanism underlying the protective function of CeO2NPs against RF in the male reproductive system are required.
Keywords: CeO2NPs radiofrequency radiation; Leydig cell; antioxidant; clock genes; testosterone synthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

