Removal of 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid from water and organic by-product minimization by catalytic ozonation
- PMID: 31297204
- PMCID: PMC6582182
- DOI: 10.1007/s40201-018-00329-8
Removal of 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid from water and organic by-product minimization by catalytic ozonation
Abstract
Background: 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-DCPA acid) is a toxic herbicide. Earlier studies to remove 2,4-DCPA acid from water used expensive and/or toxic reagents, resulting in the formation of toxic organic by-products (Org-BPs). This study evaluates the removal of 2,4-DCPA acid from aqueous media using uncatalysed and catalytic ozonation with Fe doped with Ni and Co respectively.
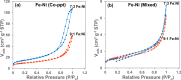
Methods: Mixed metal oxides of Ni and Co loaded on Fe respectively, prepared by co-precipitation and physical mixing were used as catalyst for ozone facilitated oxidation degradation of 2,4-DCPA acid. Their surface properties were determined by employing SEM, BET and NH3-TPD. HPLC, IC and TOC data were used for quantifying substrate and oxidation products.
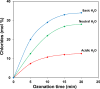
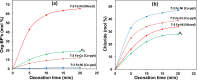
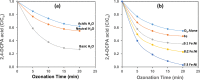
Results: Conversion of 2,4-DCPA acid increased from 38% in acidic water to 73% in basic water, however, only 26% of the total carbon was removed and 9.5% in the form of Org-BPs. With 7:3 Fe:Ni (Co-ppt) catalyst (surface area 253 m2 g-1; particle size 236 nm), 97% of pollutant was converted. Most importantly, 92% of carbon was removed and Org-BP formation was minimized to 1.5%. With 7:3 Fe:Ni (Mixed) catalyst (surface area 12 m2 g-1; particle size 1274 nm), 68% of 2,4-DCPA acid was converted, while 23% of TOC was removed, however, 66% of Org-BP's still remained.
Conclusion: In uncatalysed ozonation degradation of 2,4-DCPA acid improved with the increase in hydroxide ion concentration. Ozonation in presence of 7:3 Fe:Ni (Co-ppt) catalyst resulted in highest activity for dechlorination, TOC removal and Org-BP minimization, thus improving the quality of contaminated water.
Keywords: 7:3 Fe:Ni (co-ppt); Catalytic ozonation; Organic by-products; Total organic carbon.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures







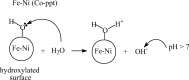


Similar articles
-
Three-dimensional Co/Ni bimetallic organic frameworks for high-efficient catalytic ozonation of atrazine: Mechanism, effect parameters, and degradation pathways analysis.Chemosphere. 2020 Aug;253:126767. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126767. Epub 2020 Apr 12. Chemosphere. 2020. PMID: 32464763
-
Catalytic ozonation of p-chlorobenzoic acid by activated carbon and nickel supported activated carbon prepared from petroleum coke.J Hazard Mater. 2009 Apr 15;163(1):115-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.06.068. Epub 2008 Jun 26. J Hazard Mater. 2009. PMID: 18667273
-
Catalytic ozonation of dimethyl phthalate over cerium supported on activated carbon.J Hazard Mater. 2009 Oct 15;170(1):411-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.04.081. Epub 2009 May 4. J Hazard Mater. 2009. PMID: 19467775
-
Fe-Mn bi-metallic oxides loaded on granular activated carbon to enhance dye removal by catalytic ozonation.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016 Sep;23(18):18800-8. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-7030-5. Epub 2016 Jun 18. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27316651
-
Catalytic ozonation for water and wastewater treatment: Recent advances and perspective.Sci Total Environ. 2020 Feb 20;704:135249. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135249. Epub 2019 Nov 22. Sci Total Environ. 2020. PMID: 31837842 Review.
References
-
- Rahnama-Moghadam S, Hillis LD, Lange RA. Chapter 3 - environmental toxins and the heart A2 - Ramachandran, Meenakshisundaram, in Heart and toxins. Boston: Academic Press; 2015. pp. 75–132.
-
- Khoshnood M, Azizian S. Adsorption of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid pesticide by graphitic carbon nanostructures prepared from biomasses. J Ind Eng Chem. 2012;18(5):1796–1800.
-
- Bekbölet M, Yenigün O, Yücel I. Sorption studies of 2,4-D on selected soils. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1999;111(1):75–88.
-
- Tsyganok AI, Otsuka K. Selective dechlorination of chlorinated phenoxy herbicides in aqueous medium by electrocatalytic reduction over palladium-loaded carbon felt. Appl Catal B Environ. 1999;22(1):15–26.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

