Depletion of Host Cell Focal Adhesion Kinase Increases the Susceptibility to Invasion by Trypanosoma cruzi Metacyclic Forms
- PMID: 31297342
- PMCID: PMC6607697
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00231
Depletion of Host Cell Focal Adhesion Kinase Increases the Susceptibility to Invasion by Trypanosoma cruzi Metacyclic Forms
Abstract
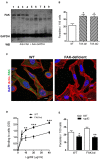
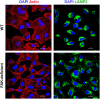
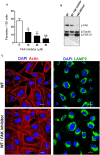
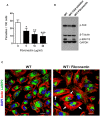
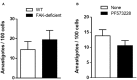
Focal adhesion kinase (FAK), a cytoplasmic protein tyrosine kinase (PTK), is implicated in diverse cellular processes, including the regulation of F-actin dynamics. Host cell F-actin rearrangement is critical for invasion of Trypanosoma cruzi, the protozoan parasite that causes Chagas disease. It is unknown whether FAK is involved in the internalization process of metacyclic trypomastigote (MT), the parasite form that is important for vectorial transmission. MT can enter the mammalian host through the ocular mucosa, lesion in the skin, or by the oral route. Oral infection by MT is currently a mode of transmission responsible for outbreaks of acute Chagas disease. Here we addressed the question by generating HeLa cell lines deficient in FAK. Host cell invasion assays showed that, as compared to control wild type (WT) cells, FAK-deficient cells were significantly more susceptible to parasite invasion. Lysosome spreading and a disarranged actin cytoskeleton, two features associated with susceptibility to MT invasion, were detected in FAK-deficient cells, as opposed to WT cells that exhibited a more organized F-actin arrangement, and lysosomes concentrated in the perinuclear area. As compared to WT cells, the capacity of FAK-deficient cells to bind a recombinant protein based on gp82, the MT surface molecule that mediates invasion, was higher. On the other hand, when treated with FAK-specific inhibitor PF573228, WT cells exhibited a dense meshwork of actin filaments, lysosome accumulation around the nucleus, and had increased resistance to MT invasion. In cells treated with PF573228, the phosphorylation levels of FAK were reduced and, as a consequence of FAK inactivation, diminished phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases (ERK1/2) was observed. Fibronectin, known to impair MT invasion, induced the formation of thick bundles of F-actin and ERK1/2 dephosphorylation.
Keywords: Trypanosoma cruzi; actin cytoskeleton; focal adhesion kinase; host cell invasion; lysosome distribution; metacyclic trypomastigote.
Figures
References
-
- Brener Z., Chiari E. (1963). Variacões morfol6gicas observadas em diferentes amostras de Trypanosoma cruzi. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 5, 220–224. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

