Inguinal hernia surgery in Korea: nationwide data from 2007-2015
- PMID: 31297352
- PMCID: PMC6609419
- DOI: 10.4174/astr.2019.97.1.41
Inguinal hernia surgery in Korea: nationwide data from 2007-2015
Abstract
Purpose: The aim of this study is to analyze inguinal hernia in Korea based on the nationwide data.
Methods: Retrospective analysis of nationwide data obtained from the Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service database for surgical repair of inguinal hernia from January, 2007 to December, 2015 was performed.
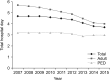
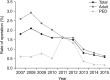
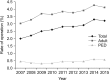
Results: A total of 314,238 cases of inguinal hernia surgery were performed during 9 years. The mean number of inguinal hernia surgery per year was 34,604 (range, 30,065-36,928). The proportion of male patient was 87%. Patients between the age of 1 to 5 years (17.3%) and of 60 to 69 years (17.4%) constituted the 2 dominant groups for inguinal hernia repair. A slight increase in repair for recurrent inguinal hernia, 1.9% to 3.2%, was observed from 2007 to 2015. The rate of concurrent bowel resection decreased from 1.9% to 0.6%. The total cost of inguinal hernia surgery was increased up to 1.68 times from 2007 to 2015 ($856 to $1,439), although the number of hospital days was decreased from 4.7 to 3.7 days. The rate of laparoscopic surgery was increased to 29.5% in 2015.
Conclusion: A mean number of 34,604 cases of inguinal hernia surgery have been carried out annually in Korea. The age distribution for inguinal hernia repair demonstrates bimodal peak at early childhood and old age. The proportion of laparoscopic surgery of inguinal hernia has been increasing for the past 9 years. The length of hospital stay and the rate of combined bowel resection have decreased.
Keywords: Diagnosis-related groups; Inguinal hernia; Nationwide.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures






References
-
- Bay-Nielsen M, Kehlet H, Strand L, Malmstrom J, Andersen FH, Wara P, et al. Quality assessment of 26,304 herniorrhaphies in Denmark: a prospective nationwide study. Lancet. 2001;358:1124–1128. - PubMed
-
- Rutkow IM. Demographic and socioeconomic aspects of hernia repair in the United States in 2003. Surg Clin North Am. 2003;83:1045–1051. - PubMed
-
- Beard JH, Oresanya LB, Ohene-Yeboah M, Dicker RA, Harris HW. Characterizing the global burden of surgical disease: a method to estimate inguinal hernia epidemiology in Ghana. World J Surg. 2013;37:498–503. - PubMed
-
- Kwon S, Lee TJ, Kim CY. Republic of Korea health system review. Geneva (Switzerland): World Health Organization; 2015.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

