Congenital hiatus hernia: A case series
- PMID: 31297485
- PMCID: PMC6593919
- DOI: 10.14744/nci.2018.58672
Congenital hiatus hernia: A case series
Abstract
Objective: Hiatus hernia is frequent in adults and rare in children; congenital hiatus hernia is even rarer. In this study, we describe a group of infants with congenital hiatus hernia and discuss its management.
Methods: Records of patients (male: 3, female: 4) who were diagnosed with congenital hiatus hernia between 2010 and 2016 were extracted. Demographic data, presenting symptoms, diagnostic investigations, operative details, postoperative follow-up, and early and late postoperative complications were evaluated retrospectively.
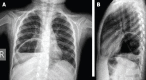
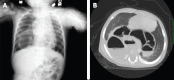
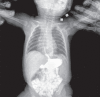
Results: Four patients were female and three were male. One patient was diagnosed prenatally while the mean age at diagnosis for others was 18.6 months. Four patients had type IV hernia, 2 had type III hernia, and one had type I hernia. The diagnosis was confirmed by chest X-ray, computerized tomography (CT) and/or upper gastrointestinal series. The hiatal repair was done in all patients either by laparotomy or laparoscopy. During the procedure, 2 patients had Nissen fundoplication and 3 patients had Thal fundoplication. Recurrence of hernia occurred in the 2 patients who had Thal fundoplication.
Conclusion: Recurrence of sliding hernias with Thal fundoplication seem more frequent in the series. If the esophagogastric junction is present in the thorax, mediastinal dissection of the esophagus may be required to achieve a good abdominal esophagus structure, which will prevent a recurrence.
Keywords: Congenital; Nissen fundoplication; Thal fundoplication; hiatus hernia; short esophagus.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: No conflict of interest was declared by the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Karpelowsky JS, Wieselthaler N, Rode H. Primary paraesophageal hernia in children. J Pediatr Surg. 2006;41:1588–93. - PubMed
-
- Avansino JR, Lorenz ML, Hendrickson M, Jolley SG. Characterization and management of paraesophageal hernias in children after antireflux operation. J Pediatr Surg. 1999;34:1610–4. - PubMed
-
- Imamoğlu M, Cay A, Koşucu P, Ozdemir O, Orhan F, Sapan L, et al. Congenital paraesophageal hiatal hernia:pitfalls in the diagnosis and treatment. J Pediatr Surg. 2005;40:1128–33. - PubMed
-
- Yousef Y, Lemoine C, St-Vil D, Emil S. Congenital paraesophageal hernia:The Montreal experience. J Pediatr Surg. 2015;50:1462–6. - PubMed
-
- Akbulut UE, Sağ E, Çakır M. Evaluation of esophageal pathology in children who underwent esophagogastroduodenoscopy. Turkish J Pediatr Dis. 2017;1:9–14.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
