Introductory Biology in Social Context: The Effects of an Issues-Based Laboratory Course on Biology Student Motivation
- PMID: 31298623
- PMCID: PMC6755311
- DOI: 10.1187/cbe.18-07-0110
Introductory Biology in Social Context: The Effects of an Issues-Based Laboratory Course on Biology Student Motivation
Abstract
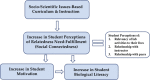
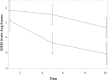
We investigated the effects of a laboratory curriculum developed using the socio--scientific issues (SSI) framework to contextualize scientific and socially relevant issues for students. Using self-determination theory and hierarchical linear modeling, we examined the effects of the SSI curriculum relative to a control curriculum on student motivation in a large introductory biology course for life science majors. The SSI group had a significant increase in motivation for engaging in the laboratory work relative to motivation of the control group. Additionally, the SSI group showed higher levels of more autonomous forms of regulation concerning participation in laboratory tasks compared with the control group. Interestingly, the SSI-based curriculum seemed to have a buffering effect on typically observed decreases in student motivation over the course of a term. This buffering effect could potentially indicate greater self-determination in students experiencing an SSI-based curriculum, which could lead to greater student success and persistence. Qualitative data suggest that this increased motivation of the SSI group relative to the control group is due to enhanced feelings of relatedness experienced by students, likely due to the SSI.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development and Evaluation of the Tigriopus Course-Based Undergraduate Research Experience: Impacts on Students' Content Knowledge, Attitudes, and Motivation in a Majors Introductory Biology Course.CBE Life Sci Educ. 2016 winter;15(4):ar72. doi: 10.1187/cbe.15-11-0228. CBE Life Sci Educ. 2016. PMID: 27909022 Free PMC article.
-
An introductory biology research-rich laboratory course shows improvements in students' research skills, confidence, and attitudes.PLoS One. 2021 Dec 16;16(12):e0261278. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0261278. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34914796 Free PMC article.
-
Student Anxiety and Perception of Difficulty Impact Performance and Persistence in Introductory Biology Courses.CBE Life Sci Educ. 2019 Jun;18(2):ar21. doi: 10.1187/cbe.17-12-0284. CBE Life Sci Educ. 2019. PMID: 31120397 Free PMC article.
-
A fully integrated undergraduate introductory biology and chemistry course with a community-based focus II: Assessment of course effectiveness.Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2021 Sep;49(5):737-747. doi: 10.1002/bmb.21555. Epub 2021 Jul 17. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2021. PMID: 34272806
-
Guiding students to think critically about reproductive development and public conversations on sex and gender.Dev Biol. 2025 Apr;520:239-250. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2024.09.012. Epub 2024 Oct 5. Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 39374891 Review.
Cited by
-
Inquiry-Team-Based Lab Course Design Enhances Underrepresented Undergraduate Predictors of Persistence in the Sciences.Med Sci Educ. 2024 Mar 1;34(3):571-580. doi: 10.1007/s40670-024-02014-y. eCollection 2024 Jun. Med Sci Educ. 2024. PMID: 38887415 Free PMC article.
-
Students' perceptions of social issues in biology courses.J Microbiol Biol Educ. 2024 Apr 25;25(1):e0019423. doi: 10.1128/jmbe.00194-23. Epub 2024 Feb 27. J Microbiol Biol Educ. 2024. PMID: 38661399 Free PMC article.
-
Maintaining Student Engagement during an Abrupt Instructional Transition: Lessons Learned from COVID-19.J Microbiol Biol Educ. 2021 Mar 31;22(1):22.1.47. doi: 10.1128/jmbe.v22i1.2305. eCollection 2021. J Microbiol Biol Educ. 2021. PMID: 33884096 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of a First-Year Place-Based Learning Community on STEM Students' Academic Achievement in their Second, Third, and Fourth Years.Innov High Educ. 2023;48(1):169-195. doi: 10.1007/s10755-022-09616-7. Epub 2022 Aug 18. Innov High Educ. 2023. PMID: 36741826 Free PMC article.
-
Connecting Theory to Practice: Using Self-Determination Theory To Better Understand Inclusion in STEM.J Microbiol Biol Educ. 2020 Apr 10;21(1):21.1.32. doi: 10.1128/jmbe.v21i1.1955. eCollection 2020. J Microbiol Biol Educ. 2020. PMID: 32431768 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albe V. (2008). When scientific knowledge, daily life experience, epistemological and social considerations intersect: Students’ argumentation in group discussion on a socio-scientific issue. Research in Science Education, , 67–90.
-
- Amabile T. M. (1993). Motivational synergy: Toward new conceptualizations of intrinsic and extrinsic motivation in the workplace. Human Resource Management Review, , 185–201. 10.1016/1053-4822(93)90012-S - DOI
-
- American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS). (1989). Science for all Americans. New York: Oxford University Press.
-
- Auerbach C. F., Silverstein L. B. (2003). Qualitative data: An introduction to coding and analysis. New York: NYU Press.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

