Effects of Short-Term Fasting and Different Overfeeding Diets on Thyroid Hormones in Healthy Humans
- PMID: 31298652
- PMCID: PMC6864752
- DOI: 10.1089/thy.2019.0237
Effects of Short-Term Fasting and Different Overfeeding Diets on Thyroid Hormones in Healthy Humans
Abstract
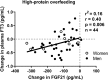
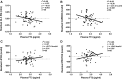
Background: A greater decrease in 24-hour energy expenditure (EE) during fasting and a smaller increase in 24-hour EE during low-protein overfeeding (metabolic "thrifty" phenotype) predict weight gain. As thyroid hormones (TH) are implicated in energy intake and metabolism, we assessed whether: (i) TH concentrations are altered by 24-hour fasting or overfeeding diets with varying protein content and (ii) diet-related changes in TH correlate with concomitant changes in EE. Methods: Fifty-eight euthyroid healthy subjects with normal glucose regulation underwent 24-hour dietary interventions including fasting, eucaloric feeding, and five overfeeding diets in a crossover design within a whole-room indirect calorimeter to measure the 24-hour EE. Overfeeding diets (200% of energy requirements) included three diets with 20% protein, one diet with 3% protein (low-protein overfeeding diet [LPF]: 46% fat), and one diet with 30% protein (high-protein overfeeding diet [HPF]: 44% fat, n = 51). Plasma free thyroxine (fT4), free triiodothyronine (fT3), and fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) concentrations were measured after overnight fast the morning of and after each diet. Results: On average, fT4 increased by 8% (+0.10 ng/dL, 95% confidence interval [CI 0.07-0.13], p < 0.0001) and fT3 decreased by 6% (-0.17 pg/mL [CI -0.27 to -0.07], p = 0.001) after 24-hour fasting, whereas both fT4 and fT3 decreased by 5% (-0.07 ng/dL [CI -0.11 to -0.04], p < 0.0001) and 4% (-0.14 pg/mL [CI -0.24 to -0.04], p = 0.008) following HPF, respectively. Greater decreases in fT3 after HPF are associated with larger decreases in FGF21 (r = 0.40, p = 0.005). Following LPF, the mean fT3 increased by 6% (+0.14 pg/mL [CI 0.05-0.2], p = 0.003) with no change in fT4 (p = 0.7). No changes in TH were observed after normal-protein overfeeding diets (all p > 0.1). No associations were observed between TH concentrations and diet-related changes in 24-hour EE during any diet (all p > 0.07). Conclusions: Acute (200%) short-term (24 hours) changes in food intake induce small changes in TH concentrations only after diets with low (0% fasting and 3% protein overfeeding) or high (30% protein overfeeding) protein content. The fT3-FGF21 association after high-protein overfeeding suggests a role for TH in inhibiting FGF21 secretion by the liver during protein excess. These results indicate that TH are involved in protein metabolism; however, they do not mediate the short-term EE response to diets that characterize the metabolic phenotypes and determine the individual susceptibility to weight gain.
Keywords: FGF21; energy expenditure; fasting; high-protein overfeeding; low-protein overfeeding; substrate oxidation; thyroid hormones.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Ng M, Fleming T, Robinson M, Thomson B, Graetz N, Margono C, Mullany EC, Biryukov S, Abbafati C, Abera SF. 2014. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 384:766–781 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stock MJ. 1999. Gluttony and thermogenesis revisited. Int J Obes 23:1105 - PubMed
-
- Dulloo A, Jacquet J. 1999. Low-protein overfeeding: a tool to unmask susceptibility to obesity in humans. Int J Obes 23:1118 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

