The structural biology of the dynamin-related proteins: New insights into a diverse, multitalented family
- PMID: 31298797
- PMCID: PMC6876869
- DOI: 10.1111/tra.12676
The structural biology of the dynamin-related proteins: New insights into a diverse, multitalented family
Abstract
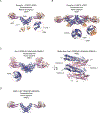
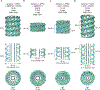
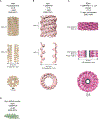
Dynamin-related proteins are multidomain, mechanochemical GTPases that self-assemble and orchestrate a wide array of cellular processes. Over the past decade, structural insights from X-ray crystallography and cryo-electron microscopy have reshaped our mechanistic understanding of these proteins. Here, we provide a historical perspective on these advances that highlights the structural attributes of different dynamin family members and explores how these characteristics affect GTP hydrolysis, conformational coupling and oligomerization. We also discuss a number of lingering challenges remaining in the field that suggest future directions of study.
Keywords: BSE; GTPase; bundle signaling element; dynamin; dynamin-related proteins; helix.
© 2019 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

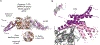

Similar articles
-
Crystal structure of the GTPase domain and the bundle signalling element of dynamin in the GDP state.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Jan 1;469(1):76-80. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.11.074. Epub 2015 Nov 21. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016. PMID: 26612256
-
Invited review: Mechanisms of GTP hydrolysis and conformational transitions in the dynamin superfamily.Biopolymers. 2016 Aug;105(8):580-93. doi: 10.1002/bip.22855. Biopolymers. 2016. PMID: 27062152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and function of conformational dynamics in the multidomain GTPase dynamin.EMBO J. 2016 Feb 15;35(4):443-57. doi: 10.15252/embj.201593477. Epub 2016 Jan 18. EMBO J. 2016. PMID: 26783363 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis of oligomerization in the stalk region of dynamin-like MxA.Nature. 2010 May 27;465(7297):502-6. doi: 10.1038/nature08972. Epub 2010 Apr 28. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20428112
-
Building a fission machine--structural insights into dynamin assembly and activation.J Cell Sci. 2013 Jul 1;126(Pt 13):2773-84. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108845. Epub 2013 Jun 18. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 23781021 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The hypervariable region of atlastin-1 is a site for intrinsic and extrinsic regulation.J Cell Biol. 2021 Nov 1;220(11):e202104128. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202104128. Epub 2021 Sep 21. J Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 34546351 Free PMC article.
-
A dynamin superfamily-like pseudoenzyme coordinates with MICOS to promote cristae architecture.Curr Biol. 2024 Jun 17;34(12):2606-2622.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2024.04.028. Epub 2024 Apr 30. Curr Biol. 2024. PMID: 38692277 Free PMC article.
-
SynDLP is a dynamin-like protein of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 with eukaryotic features.Nat Commun. 2023 Apr 14;14(1):2156. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37746-9. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37059718 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstitution of human atlastin fusion activity reveals autoinhibition by the C terminus.J Cell Biol. 2022 Feb 7;221(2):e202107070. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202107070. Epub 2021 Nov 24. J Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 34817557 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative modeling of guanylate binding protein dimers.Protein Sci. 2023 Dec;32(12):e4818. doi: 10.1002/pro.4818. Protein Sci. 2023. PMID: 37916607 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Praefcke GJ, McMahon HT. The dynamin superfamily: universal membrane tubulation and fission molecules? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5(2):133–147. - PubMed
-
- Hoppins S, Lackner L, Nunnari J. The machines that divide and fuse mitochondria. Annu Rev Biochem. 2007;76:751–780. - PubMed
-
- Ferguson KM, Lemmon MA, Schlessinger J, Sigler PB. Crystal structure at 2.2 A resolution of the pleckstrin homology domain from human dynamin. Cell. 1994;79(2):199–209. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

