A set of Arabidopsis genes involved in the accommodation of the downy mildew pathogen Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis
- PMID: 31299058
- PMCID: PMC6625732
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007747
A set of Arabidopsis genes involved in the accommodation of the downy mildew pathogen Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis
Abstract
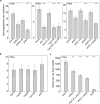
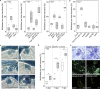
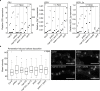
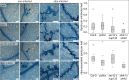
The intracellular accommodation structures formed by plant cells to host arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi and biotrophic hyphal pathogens are cytologically similar. Therefore we investigated whether these interactions build on an overlapping genetic framework. In legumes, the malectin-like domain leucine-rich repeat receptor kinase SYMRK, the cation channel POLLUX and members of the nuclear pore NUP107-160 subcomplex are essential for symbiotic signal transduction and arbuscular mycorrhiza development. We identified members of these three groups in Arabidopsis thaliana and explored their impact on the interaction with the oomycete downy mildew pathogen Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis (Hpa). We report that mutations in the corresponding genes reduced the reproductive success of Hpa as determined by sporangiophore and spore counts. We discovered that a developmental transition of haustorial shape occurred significantly earlier and at higher frequency in the mutants. Analysis of the multiplication of extracellular bacterial pathogens, Hpa-induced cell death or callose accumulation, as well as Hpa- or flg22-induced defence marker gene expression, did not reveal any traces of constitutive or exacerbated defence responses. These findings point towards an overlap between the plant genetic toolboxes involved in the interaction with biotrophic intracellular hyphal symbionts and pathogens in terms of the gene families involved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An Arabidopsis (malectin-like) leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase contributes to downy mildew disease.Plant Cell Environ. 2011 Nov;34(11):1944-57. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2011.02390.x. Epub 2011 Jul 25. Plant Cell Environ. 2011. PMID: 21711359
-
Arabidopsis downy mildew effector HaRxL106 suppresses plant immunity by binding to RADICAL-INDUCED CELL DEATH1.New Phytol. 2018 Oct;220(1):232-248. doi: 10.1111/nph.15277. New Phytol. 2018. PMID: 30156022 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple candidate effectors from the oomycete pathogen Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis suppress host plant immunity.PLoS Pathog. 2011 Nov;7(11):e1002348. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002348. Epub 2011 Nov 3. PLoS Pathog. 2011. PMID: 22072967 Free PMC article.
-
Hyaloperonospora Arabidopsidis as a pathogen model.Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2010;48:329-45. doi: 10.1146/annurev-phyto-080508-094422. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2010. PMID: 19400636 Review.
-
Focal accumulation of defences at sites of fungal pathogen attack.J Exp Bot. 2008;59(13):3501-8. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ern205. Epub 2008 Aug 13. J Exp Bot. 2008. PMID: 18703493 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
IPD3, a master regulator of arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis, affects genes for immunity and metabolism of non-host Arabidopsis when restored long after its evolutionary loss.Plant Mol Biol. 2024 Feb 18;114(2):21. doi: 10.1007/s11103-024-01422-3. Plant Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38368585 Free PMC article.
-
An Arabidopsis downy mildew non-RxLR effector suppresses induced plant cell death to promote biotroph infection.J Exp Bot. 2021 Feb 2;72(2):718-732. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eraa472. J Exp Bot. 2021. PMID: 33063828 Free PMC article.
-
A combination of chitooligosaccharide and lipochitooligosaccharide recognition promotes arbuscular mycorrhizal associations in Medicago truncatula.Nat Commun. 2019 Nov 6;10(1):5047. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12999-5. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31695035 Free PMC article.
-
Oomycete small RNAs bind to the plant RNA-induced silencing complex for virulence.Elife. 2020 May 22;9:e56096. doi: 10.7554/eLife.56096. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32441255 Free PMC article.
-
Stop helping pathogens: engineering plant susceptibility genes for durable resistance.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2021 Aug;70:187-195. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2021.05.005. Epub 2021 Jun 19. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34153774 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Genre A, Chabaud M, Faccio A, Barker DG, Bonfante P. Prepenetration apparatus assembly precedes and predicts the colonization patterns of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi within the root cortex of both Medicago truncatula and Daucus carota. Plant Cell. 2008;20: 1407–1420. 10.1105/tpc.108.059014 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

