Assessment of Mumps Virus-Specific Antibodies: Comparison of Plaque Reduction Neutralization Test and Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay Estimates
- PMID: 31299077
- PMCID: PMC6761965
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiz345
Assessment of Mumps Virus-Specific Antibodies: Comparison of Plaque Reduction Neutralization Test and Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay Estimates
Abstract
Background: The plaque reduction neutralization test (PRNT), which measures a subset of immunoglobulin antibodies (functional neutralizing antibodies), and the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), which measures total immunoglobulin (neutralizing and nonneutralizing antibodies), characterize different aspects of the anti-mumps virus antibody response after vaccination.
Methods: Data from a recent phase 3 clinical trial (NCT01681992) of 2 measles-mumps-rubella vaccines were used to compare anti-mumps antibody responses measured using an unenhanced PRNT (GSK; seropositivity cutoff and threshold, 2.5 and 4 times the 50% end-point dilution, respectively) with those estimated using an ELISA (thresholds, 5 and 10 ELISA units/mL, respectively).
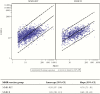
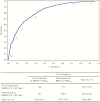
Results: Of 3990 initially seronegative samples, 3284 (82.3%) were seropositive after vaccination for anti-mumps antibodies in both assays. The Pearson correlation coefficient for double-positive samples was 0.57, indicative of a moderate correlation. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis showed that an ELISA threshold of 51.7 ELISA units/mL best corresponded to the PRNT seroresponse threshold. There was no obvious vaccine brand effect on the correlation between assays.
Conclusions: The moderate correlation between the anti-mumps antibody measurements obtained with PRNT and ELISA reflects different aspects of the serological response. In the absence of a well-defined protective serological threshold, PRNT provides complementary information on the antibody response, whereas ELISA remains a critically useful measurement of vaccine immunogenicity.
Keywords: enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; mumps; plaque reduction neutralization test; seropositive; seroresponse; vaccine.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Immunogenicity and safety of measles-mumps-rubella vaccine at two different potency levels administered to healthy children aged 12-15 months: A phase III, randomized, non-inferiority trial.Vaccine. 2018 Sep 11;36(38):5781-5788. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2018.07.076. Epub 2018 Aug 10. Vaccine. 2018. PMID: 30104117 Clinical Trial.
-
Two-year antibody persistence in children vaccinated at 12-15 months with a measles-mumps-rubella virus vaccine without human serum albumin.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2017 Jul 3;13(7):1516-1522. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2017.1309486. Epub 2017 May 8. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2017. PMID: 28481690 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Antibody persistence after primary measles-mumps-rubella vaccine and response to a second dose given at four to six vs. eleven to thirteen years.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1996 Aug;15(8):687-92. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199608000-00010. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1996. PMID: 8858673
-
Evaluation of the focus reduction neutralization and ELISA tests compared to the plaque reduction neutralization test for the detection of antibodies against measles virus.Biologicals. 2024 Nov;88:101795. doi: 10.1016/j.biologicals.2024.101795. Epub 2024 Oct 5. Biologicals. 2024. PMID: 39369472
-
Comparison of measles IgG enzyme immunoassays (EIA) versus plaque reduction neutralization test (PRNT) for measuring measles serostatus: a systematic review of head-to-head analyses of measles IgG EIA and PRNT.BMC Infect Dis. 2023 May 31;23(1):367. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08199-8. BMC Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37259032 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Booster doses of an inactivated F genotype mumps vaccine enhance immunogenicity in mice.Vaccine X. 2024 Jan 13;17:100437. doi: 10.1016/j.jvacx.2024.100437. eCollection 2024 Mar. Vaccine X. 2024. PMID: 38317857 Free PMC article.
-
Response to Vaccination against Mumps in Medical Students: Two Doses Are Needed.Viruses. 2021 Jul 7;13(7):1311. doi: 10.3390/v13071311. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34372517 Free PMC article.
-
Serologic Cross-Reactivity between the Mumps Virus Vaccine Genotype A Strain and the Circulating Genotype G Strain.Viruses. 2024 Sep 8;16(9):1434. doi: 10.3390/v16091434. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39339910 Free PMC article.
-
Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus Antibodies among Livestock on Corsica, France, 2014-2016.Emerg Infect Dis. 2020 May;26(5):1041-1044. doi: 10.3201/10.3201/eid2605.191465. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32310061 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rubin SA, Qi L, Audet SA, et al. . Antibody induced by immunization with the Jeryl Lynn mumps vaccine strain effectively neutralizes a heterologous wild-type mumps virus associated with a large outbreak. J Infect Dis 2008; 198:508–15. - PubMed
-
- Cortese MM, Barskey AE, Tegtmeier GE, et al. . Mumps antibody levels among students before a mumps outbreak: in search of a correlate of immunity. J Infect Dis 2011; 204:1413–22. - PubMed

