The genetic and clinico-pathological profile of early-onset progressive supranuclear palsy
- PMID: 31299107
- PMCID: PMC6790973
- DOI: 10.1002/mds.27786
The genetic and clinico-pathological profile of early-onset progressive supranuclear palsy
Abstract
Background: Studies on early-onset presentations of progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) have been limited to those where a rare monogenic cause has been identified. Here, we have defined early-onset PSP (EOPSP) and investigated its genetic and clinico-pathological profile in comparison with late-onset PSP (LOPSP) and Parkinson's disease (PD).
Methods: We included subjects from the Queen Square Brain Bank, PROSPECT-UK study, and Tracking Parkinson's study. Group comparisons of data were made using Welch's t-test and Kruskal-Wallis analysis of variance. EOPSP was defined as the youngest decile of motor age at onset (≤55 years) in the Queen Square Brain Bank PSP case series.
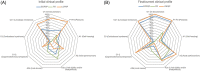
Results: We identified 33 EOPSP, 328 LOPSP, and 2000 PD subjects. The early clinical features of EOPSP usually involve limb parkinsonism and gait freezing, with 50% of cases initially misdiagnosed as having PD. We found that an initial clinical diagnosis of EOPSP had lower diagnostic sensitivity (33%) and positive predictive value (38%) in comparison with LOPSP (80% and 76%) using a postmortem diagnosis of PSP as the gold standard. 3/33 (9%) of the EOPSP group had an underlying monogenic cause. Using a PSP genetic risk score (GRS), we showed that the genetic risk burden in the EOPSP (mean z-score, 0.59) and LOPSP (mean z-score, 0.48) groups was significantly higher (P < 0.05) when compared with the PD group (mean z-score, -0.08).
Conclusions: The initial clinical profile of EOPSP is often PD-like. At the group level, a PSP GRS was able to differentiate EOPSP from PD, and this may be helpful in future diagnostic algorithms. © 2019 The Authors. Movement Disorders published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Keywords: Parkinson's disease/parkinsonism; clinical neurology; genetics; progressive supranuclear palsy.
© 2019 The Authors. Movement Disorders published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Figures
References
-
- Schrag A, Ben‐Shlomo Y, Quinn NP. Prevalence of progressive supranuclear palsy and multiple system atrophy: a cross‐sectional study. Lancet 1999;354(9192):1771–1775. - PubMed
-
- Spillantini MG, Goedert M. Tau pathology and neurodegeneration. Lancet Neurol 2013;12(6):609–622. - PubMed
-
- Steele JC, Richardson JC, Olszewski J. Progressive supranuclear palsy: a heterogeneous degeneration involving the brain stem, basal ganglia and cerebellum with vertical gaze and pseudobulbar palsy, nuchal dystonia and dementia. Arch Neurol 1964;10(1):333–359. - PubMed
-
- Nath U, Ben‐Shlomo Y, Thomson RG, Lees AJ, Burn DJ. Clinical features and natural history of progressive supranuclear palsy: a clinical cohort study. Neurology 2003;60(6):910–916. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

