Alternative polyadenylation produces multiple 3' untranslated regions of odorant receptor mRNAs in mouse olfactory sensory neurons
- PMID: 31299892
- PMCID: PMC6624953
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-019-5927-3
Alternative polyadenylation produces multiple 3' untranslated regions of odorant receptor mRNAs in mouse olfactory sensory neurons
Abstract
Background: Odorant receptor genes constitute the largest gene family in mammalian genomes and this family has been extensively studied in several species, but to date far less attention has been paid to the characterization of their mRNA 3' untranslated regions (3'UTRs). Given the increasing importance of UTRs in the understanding of RNA metabolism, and the growing interest in alternative polyadenylation especially in the nervous system, we aimed at identifying the alternative isoforms of odorant receptor mRNAs generated through 3'UTR variation.
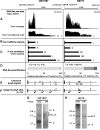
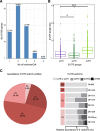
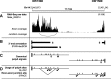
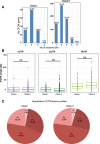
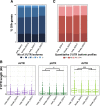
Results: We implemented a dedicated pipeline using IsoSCM instead of Cufflinks to analyze RNA-Seq data from whole olfactory mucosa of adult mice and obtained an extensive description of the 3'UTR isoforms of odorant receptor mRNAs. To validate our bioinformatics approach, we exhaustively analyzed the 3'UTR isoforms produced from 2 pilot genes, using molecular approaches including northern blot and RNA ligation mediated polyadenylation test. Comparison between datasets further validated the pipeline and confirmed the alternative polyadenylation patterns of odorant receptors. Qualitative and quantitative analyses of the annotated 3' regions demonstrate that 1) Odorant receptor 3'UTRs are longer than previously described in the literature; 2) More than 77% of odorant receptor mRNAs are subject to alternative polyadenylation, hence generating at least 2 detectable 3'UTR isoforms; 3) Splicing events in 3'UTRs are restricted to a limited subset of odorant receptor genes; and 4) Comparison between male and female data shows no sex-specific differences in odorant receptor 3'UTR isoforms.
Conclusions: We demonstrated for the first time that odorant receptor genes are extensively subject to alternative polyadenylation. This ground-breaking change to the landscape of 3'UTR isoforms of Olfr mRNAs opens new avenues for investigating their respective functions, especially during the differentiation of olfactory sensory neurons.
Keywords: 3′ untranslated region; Adult olfactory mucosa; Alternative polyadenylation; IsoSCM; Odorant receptors; Olfactory sensory neuron; Olfr genes; mRNA isoforms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Shepherd GM. The olfactory glomerulus: its significance for sensory processing. In: Katsuki Y, Norgren R, Sato M, editors. Brain mechanisms of sensation. New York: Wiley; 1981. pp. 209–223.
-
- Buck L, Axel R. A novel multigene family may encode odorant receptors: a molecular basis for odor recognition. Cell. 1991;65:175–187. - PubMed
-
- Chess A, Simon I, Cedar H, Axel R. Allelic inactivation regulates olfactory receptor gene expression. Cell. 1994;78:823–834. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

