Self-injury: Treatment, Assessment, Recovery (STAR): online intervention for adolescent non-suicidal self-injury - study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 31300065
- PMCID: PMC6626324
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-019-3501-6
Self-injury: Treatment, Assessment, Recovery (STAR): online intervention for adolescent non-suicidal self-injury - study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Non-suicidal self-injury (NSSI) is a clinically significant behavior affecting approximately 18% of adolescents and young adults worldwide. The importance of NSSI is supported by its association with a broad spectrum of mental disorders. Despite its high relevance, evidence-based, specific, time-, and cost-effective treatment approaches are scarce. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) seems effective in reducing the frequency of NSSI in adolescents and young adults. However, young people are often reluctant to seek professional help and effective interventions adressing NSSI are not sufficiently available across all regions of Germany. Research indicates that the majority of youth with risk behavior (including NSSI) prefer technology-based interventions. To date, effective interventions for adolescents and young adults with NSSI that are deliverd online are not available.
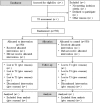
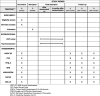
Methods: The present project aims to develop and evaluate an online intervention for adolescents and young adults with NSSI based on the content of a recently evaluated face-to-face short-term program that includes elements of CBT and dialectical behavior therapy (DBT): "The Cutting Down Programme" (CDP). The efficacy of the new online CDP intervention will be tested in a randomized controlled trial (RCT) in which n = 700 youths engaging in repetitive NSSI will participate in either an online psychoeducation (n = 350) or online CDP (n = 350). Within a postline assessment four months after baseline (end of treatment; T1), and follow-up evaluations 12 and 18 months after baseline (follow-ups; T2 and T3), NSSI and comorbid symptoms as well as quality of life will be assessed. It is hypothesized that participants receiving online CDP report a greater reduction in the frequency of NSSI within the last three months at T2 (primary endpoint) compared to those receiving online psychoeducation. Exploratory analyses will focus on predictors of treatment outcome.
Discussion: We report on the development and evaluation of an online intervention for adolescents and young adults engaging in NSSI based on the CDP. If supported by empirical evidence, an online-based intervention for NSSI might help to overcome the limited availability of adequate interventions for youth.
Trial registration: German Clinical Trials Register, DRKS00014623 . Registered on 22 May 2018.
Keywords: Adolescents; Internet; Non-suicidal self-injury; Online intervention; Randomized controlled trial.
Conflict of interest statement
PLP received a speaker’s honorarium from Shire. He was involved in clinical studies for Lundbeck and Servier. The other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition. Arlington: American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
-
- Asarnow JR, Porta G, Spirito A, Emslie G, Clarke G, Wagner KD, et al. Suicide attempts and nonsuicidal self-injury in the treatment of resistant depression in adolescents: findings from the TORDIA study. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2011;50:772–781. doi: 10.1016/j.jaac.2011.04.003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed