Liver organoids: from basic research to therapeutic applications
- PMID: 31300517
- PMCID: PMC6872443
- DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-319256
Liver organoids: from basic research to therapeutic applications
Abstract
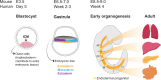
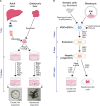
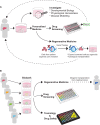
Organoid cultures have emerged as an alternative in vitro system to recapitulate tissues in a dish. While mouse models and cell lines have furthered our understanding of liver biology and associated diseases, they suffer in replicating key aspects of human liver tissue, in particular its complex architecture and metabolic functions. Liver organoids have now been established for multiple species from induced pluripotent stem cells, embryonic stem cells, hepatoblasts and adult tissue-derived cells. These represent a promising addition to our toolbox to gain a deeper understanding of this complex organ. In this perspective we will review the advances in the liver organoid field, its limitations and potential for biomedical applications.
Keywords: disease modelling; liver; organoid; personalised medicine.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2019. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Method of the Year 2017: Organoids. Nat Methods 2018;15:1 10.1038/nmeth.4575 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
