Labile Calcium-Permeable AMPA Receptors Constitute New Glutamate Synapses Formed in Hypothalamic Neuroendocrine Cells during Salt Loading
- PMID: 31300543
- PMCID: PMC6675872
- DOI: 10.1523/ENEURO.0112-19.2019
Labile Calcium-Permeable AMPA Receptors Constitute New Glutamate Synapses Formed in Hypothalamic Neuroendocrine Cells during Salt Loading
Abstract
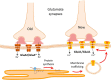
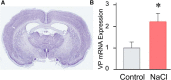
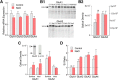
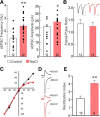
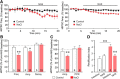
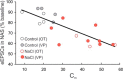
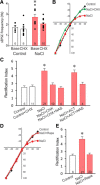
Magnocellular neuroendocrine cells (MNCs) of the hypothalamus play a critical role in the regulation of fluid and electrolyte homeostasis. They undergo a dramatic structural and functional plasticity under sustained hyperosmotic conditions, including an increase in afferent glutamatergic synaptic innervation. We tested for a postulated increase in glutamate AMPA receptor expression and signaling in magnocellular neurons of the male rat hypothalamic supraoptic nucleus (SON) induced by chronic salt loading. While without effect on GluA1-4 subunit mRNA, salt loading with 2% saline for 5-7 d resulted in a selective increase in AMPA receptor GluA1 protein expression in the SON, with no change in GluA2-4 protein expression, suggesting an increase in the ratio of GluA1 to GluA2 subunits. Salt loading induced a corresponding increase in EPSCs in both oxytocin (OT) and vasopressin (VP) neurons, with properties characteristic of calcium-permeable AMPA receptor-mediated currents. Unexpectedly, the emergent AMPA synaptic currents were silenced by blocking protein synthesis and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) activity in the slices, suggesting that the new glutamate synapses induced by salt loading require continuous dendritic protein synthesis for maintenance. These findings indicate that chronic salt loading leads to the induction of highly labile glutamate synapses in OT and VP neurons that are comprised of calcium-permeable homomeric GluA1 AMPA receptors. The glutamate-induced calcium influx via calcium-permeable AMPA receptors would be expected to play a key role in the induction and/or maintenance of activity-dependent synaptic plasticity that occurs in the magnocellular neurons during chronic osmotic stimulation.
Keywords: excitability; osmoregulation; oxytocin; paraventricular; supraoptic; vasopressin.
Copyright © 2019 Di et al.
Figures
References
-
- Al-Ghoul WM, Meeker RB, Greenwood RS (1997) Differential expression of five N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit mRNAs in vasopressin and oxytocin neuroendocrine cells. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 44:262–272. - PubMed
-
- Arnauld E, Wattiaux JP, Arsaut J, Rostène W, Vincent JD (1993) Alterations in vasopressin and oxytocin messenger RNA in the rat supraoptic nucleus during dehydration-rehydration evaluated by in situ hybridization and northern blotting. Neurosci Lett 149:177–181. 10.1016/0304-3940(93)90765-d - DOI - PubMed
-
- Borges K, Dingledine R (1998) AMPA receptors: molecular and functional diversity. Prog Brain Res 116:153–170. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
