VISAGE Reveals a Targetable Mitotic Spindle Vulnerability in Cancer Cells
- PMID: 31302152
- PMCID: PMC6688637
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cels.2019.05.009
VISAGE Reveals a Targetable Mitotic Spindle Vulnerability in Cancer Cells
Abstract
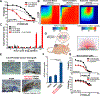
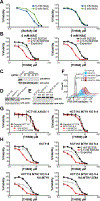
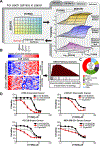
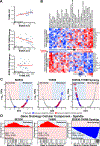
There is an unmet need for new antimitotic drug combinations that target cancer-specific vulnerabilities. Based on our finding of elevated biomolecule oxidation in mitotically arrested cancer cells, we combined Plk1 inhibitors with TH588, an MTH1 inhibitor that prevents detoxification of oxidized nucleotide triphosphates. This combination showed robust synergistic killing of cancer, but not normal, cells that, surprisingly, was MTH1-independent. To dissect the underlying synergistic mechanism, we developed VISAGE, a strategy integrating experimental synergy quantification with computational-pathway-based gene expression analysis. VISAGE predicted, and we experimentally confirmed, that this synergistic combination treatment targeted the mitotic spindle. Specifically, TH588 binding to β-tubulin impaired microtubule assembly, which when combined with Plk1 blockade, synergistically disrupted mitotic chromosome positioning to the spindle midzone. These findings identify a cancer-specific mitotic vulnerability that is targetable using Plk1 inhibitors with microtubule-destabilizing agents and highlight the general utility of the VISAGE approach to elucidate molecular mechanisms of drug synergy.
Keywords: MTH1; Plk1; TH588; anti-microtubule drugs; cancer therapy; chromosome alignment; chromosome congression; drug synergy; mitosis; tubulin.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
Michael B. Yaffe is a member of the Divisions of Surgical Oncology and Trauma and Critical Care, Department of Surgery, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, and the Chief Academic Editor of the journal Science Signaling. The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Adams PD, Afonine PV, Bunkoczi G, Chen VB, Davis IW, Echols N, Headd JJ, Hung LW, Kapral GJ, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, et al. (2010). PHENIX: a comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta crystallographica Section D, Biological crystallography 66, 213–221. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alexander J, Lim D, Joughin BA, Hegemann B, Hutchins JR, Ehrenberger T, Ivins F, Sessa F, Hudecz O, Nigg EA, et al. (2011). Spatial exclusivity combined with positive and negative selection of phosphorylation motifs is the basis for context-dependent mitotic signaling. Sci Signal 4, ra42. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alexandre J, Batteux F, Nicco C, Chereau C, Laurent A, Guillevin L, Weill B, and Goldwasser F (2006). Accumulation of hydrogen peroxide is an early and crucial step for paclitaxel-induced cancer cell death both in vitro and in vivo. Int J Cancer 119, 41–48. - PubMed
-
- Archambault V, and Glover DM (2009). Polo-like kinases: conservation and divergence in their functions and regulation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10, 265–275. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

