Short-term pharmacological activation of Nrf2 ameliorates vascular dysfunction in aged rats and in pathological human vasculature. A potential target for therapeutic intervention
- PMID: 31302408
- PMCID: PMC6626891
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101271
Short-term pharmacological activation of Nrf2 ameliorates vascular dysfunction in aged rats and in pathological human vasculature. A potential target for therapeutic intervention
Abstract
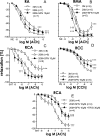
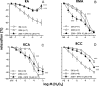
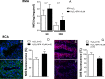
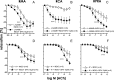
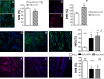
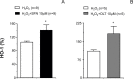
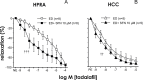
Oxidative stress contributes to endothelial dysfunction, a key step in cardiovascular disease development. Ageing-related vascular dysfunction involves defective antioxidant response. Nuclear factor erythroid 2-like-2 (Nrf2), orchestrates cellular response to oxidative stress. We evaluated the impact of Nrf2-activation on endothelium-dependent and H2O2-mediated vasodilations in: aorta (RA), mesenteric artery (RMA), coronary artery (RCA) and corpus cavernosum (RCC) from ageing rats and in human penile arteries (HPRA) and corpus cavernosum (HCC) from erectile dysfunction (ED) patients. Relaxant responses were evaluated in organ chambers and wire myographs. Nrf2 content and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) were determined by ELISA. Superoxide and Nrf2 were detected by immunofluorescence. Pharmacological activation of Nrf2 with sulforaphane (SFN) improved NO- and endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor-mediated endothelium-dependent vasodilation and H2O2-induced relaxation in vascular beds from aging rats. SFN-induced effects were associated with increased Nrf2 (RMA, RCA) and reduced superoxide detection in RCA. Improvement of vascular function was confirmed in HPRA and HCC from ED patients and mimicked by another Nrf2 activator, oltipraz. Nrf2 increase and superoxide reduction together with HO-1 increase by Nrf2 activation was evidenced in HCC from ED patients. PDE5 inhibitor-induced relaxations of HPRA and HCC from ED patients were enhanced by SFN. Nrf2 short-term pharmacological activation attenuates age-related impairment of endothelium-dependent and reactive oxygen species (ROS)-induced vasodilation in different rat and human vascular territories by upregulation of Nrf2-related signaling and decreased oxidative stress. In ED patients target tissues, Nrf2 potentiates the functional effect of ED conventional pharmacological therapy suggesting potential therapeutic implication.
Keywords: Ageing; Endothelial dysfunction; Erectile dysfunction; Human vasculature; Nrf2; Oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Diabetes exacerbates the functional deficiency of NO/cGMP pathway associated with erectile dysfunction in human corpus cavernosum and penile arteries.J Sex Med. 2010 Feb;7(2 Pt 1):758-68. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2009.01587.x. Epub 2009 Nov 12. J Sex Med. 2010. PMID: 19912487
-
Nebivolol potentiates the efficacy of PDE5 inhibitors to relax corpus cavernosum and penile arteries from diabetic patients by enhancing the NO/cGMP pathway.J Sex Med. 2014 May;11(5):1182-92. doi: 10.1111/jsm.12477. J Sex Med. 2014. PMID: 24877179
-
Nitrergic function is lost but endothelial function is preserved in the corpus cavernosum and penile resistance arteries of men after radical prostatectomy.J Sex Med. 2015 Mar;12(3):590-9. doi: 10.1111/jsm.12801. Epub 2014 Dec 21. J Sex Med. 2015. PMID: 25529966
-
Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling: An important molecular mechanism of herbal medicine in the treatment of atherosclerosis via the protection of vascular endothelial cells from oxidative stress.J Adv Res. 2021 Jul 6;34:43-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2021.06.023. eCollection 2021 Dec. J Adv Res. 2021. PMID: 35024180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Panaxatriol saponin ameliorates myocardial infarction-induced cardiac fibrosis by targeting Keap1/Nrf2 to regulate oxidative stress and inhibit cardiac-fibroblast activation and proliferation.Free Radic Biol Med. 2022 Sep;190:264-275. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.08.016. Epub 2022 Aug 14. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 35977659 Review.
Cited by
-
Repeated glucose spikes and insulin resistance synergistically deteriorate endothelial function and bardoxolone methyl ameliorates endothelial dysfunction.PLoS One. 2022 Jan 24;17(1):e0263080. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0263080. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35073378 Free PMC article.
-
The onset and the development of cardiometabolic aging: an insight into the underlying mechanisms.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 26;15:1447890. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1447890. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39391689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Onion and Apple Functional Ingredients Intake Improves Antioxidant and Inflammatory Status and Vascular Injury in Obese Zucker Rats.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Sep 29;11(10):1953. doi: 10.3390/antiox11101953. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36290676 Free PMC article.
-
"LONG COVID"-A hypothesis for understanding the biological basis and pharmacological treatment strategy.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2022 Feb;10(1):e00911. doi: 10.1002/prp2.911. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2022. PMID: 35029046 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelial cells from umbilical cord of women affected by gestational diabetes: A suitable in vitro model to study mechanisms of early vascular senescence in diabetes.FASEB J. 2021 Jun;35(6):e21662. doi: 10.1096/fj.202002072RR. FASEB J. 2021. PMID: 34046935 Free PMC article.
References
-
- El Assar M., Angulo J., Rodríguez-Mañas L. Oxidative stress and vascular inflammation in aging. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013;65:380–401. - PubMed
-
- Incalza M.A., D'Oria R., Natalicchio A., Perrini S., Laviola L., Giorgino F. Oxidative stress and reactive oxygen species in endothelial dysfunction associated with cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2018;100:1–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

