Fexofenadine inhibits TNF signaling through targeting to cytosolic phospholipase A2 and is therapeutic against inflammatory arthritis
- PMID: 31302596
- PMCID: PMC8157820
- DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215543
Fexofenadine inhibits TNF signaling through targeting to cytosolic phospholipase A2 and is therapeutic against inflammatory arthritis
Abstract
Objective: Tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) signalling plays a central role in the pathogenesis of various autoimmune diseases, particularly inflammatory arthritis. This study aimed to repurpose clinically approved drugs as potential inhibitors of TNF-α signalling in treatment of inflammatory arthritis.
Methods: In vitro and in vivo screening of an Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved drug library; in vitro and in vivo assays for examining the blockade of TNF actions by fexofenadine: assays for defining the anti-inflammatory activity of fexofenadine using TNF-α transgenic (TNF-tg) mice and collagen-induced arthritis in DBA/1 mice. Identification and characterisation of the binding of fexofenadine to cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) using drug affinity responsive target stability assay, proteomics, cellular thermal shift assay, information field dynamics and molecular dynamics; various assays for examining fexofenadine inhibition of cPLA2 as well as the dependence of fexofenadine's anti-TNF activity on cPLA2.
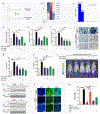
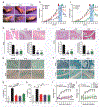
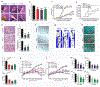
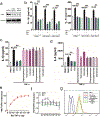
Results: Serial screenings of a library composed of FDA-approved drugs led to the identification of fexofenadine as an inhibitor of TNF-α signalling. Fexofenadine potently inhibited TNF/nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-ĸB) signalling in vitro and in vivo, and ameliorated disease symptoms in inflammatory arthritis models. cPLA2 was isolated as a novel target of fexofenadine. Fexofenadine blocked TNF-stimulated cPLA2 activity and arachidonic acid production through binding to catalytic domain 2 of cPLA2 and inhibition of its phosphorylation on Ser-505. Further, deletion of cPLA2 abolished fexofenadine's anti-TNF activity.
Conclusion: Collectively, these findings not only provide new insights into the understanding of fexofenadine action and underlying mechanisms but also provide new therapeutic interventions for various TNF-α and cPLA2-associated pathologies and conditions, particularly inflammatory rheumatic diseases.
Keywords: TNF-α; cPLA2; fexofenadine; inflammation; inflammatory arthritis.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2019. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cytosolic Phospholipase A2 Is Required for Fexofenadine's Therapeutic Effects against Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 15;22(20):11155. doi: 10.3390/ijms222011155. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34681815 Free PMC article.
-
Fexofenadine protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by targeting cytosolic phospholipase A2.Int Immunopharmacol. 2023 Mar;116:109637. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109637. Epub 2023 Feb 8. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36764283
-
Cytosolic phospholipase A2 alpha inhibitor, pyrroxyphene, displays anti-arthritic and anti-bone destructive action in a murine arthritis model.Inflamm Res. 2010 Jan;59(1):53-62. doi: 10.1007/s00011-009-0069-8. Epub 2009 Aug 5. Inflamm Res. 2010. PMID: 19655230
-
TAK1: a potent tumour necrosis factor inhibitor for the treatment of inflammatory diseases.Open Biol. 2020 Sep;10(9):200099. doi: 10.1098/rsob.200099. Epub 2020 Sep 2. Open Biol. 2020. PMID: 32873150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress of cPLA2 in cardiovascular diseases (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2025 Apr;31(4):103. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2025.13468. Epub 2025 Feb 21. Mol Med Rep. 2025. PMID: 39981923 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integration of National Health Insurance claims data and animal models reveals fexofenadine as a promising repurposed drug for Parkinson's disease.J Neuroinflammation. 2024 Feb 21;21(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s12974-024-03041-7. J Neuroinflammation. 2024. PMID: 38383441 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary pyruvate targets cytosolic phospholipase A2 to mitigate inflammation and obesity in mice.Protein Cell. 2024 Sep 1;15(9):661-685. doi: 10.1093/procel/pwae014. Protein Cell. 2024. PMID: 38512816 Free PMC article.
-
Ångstrom-scale silver particles ameliorate collagen-induced and K/BxN-transfer arthritis in mice via the suppression of inflammation and osteoclastogenesis.Inflamm Res. 2023 Nov;72(10-11):2053-2072. doi: 10.1007/s00011-023-01778-0. Epub 2023 Oct 10. Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 37816881
-
Exogenous pyruvate is therapeutic against colitis by targeting cytosolic phospholipase A2.Genes Dis. 2025 Feb 22;12(5):101571. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2025.101571. eCollection 2025 Sep. Genes Dis. 2025. PMID: 40605975 Free PMC article.
-
Fexofenadine Protects Against Intervertebral Disc Degeneration Through TNF Signaling.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Aug 24;9:687024. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.687024. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34504840 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barturen G, Beretta L, Cervera R, et al. Moving towards a molecular taxonomy of autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Nature reviews Rheumatology 2018, 14(2):75–93. - PubMed
-
- Brenner D, Blaser H, Mak TW. Regulation of tumour necrosis factor signalling: live or let die. Nat Rev Immunol 2015, 15(6):362–374. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

