Major causes of death in preterm infants in selected hospitals in Ethiopia (SIP): a prospective, cross-sectional, observational study
- PMID: 31303299
- PMCID: PMC6639243
- DOI: 10.1016/S2214-109X(19)30220-7
Major causes of death in preterm infants in selected hospitals in Ethiopia (SIP): a prospective, cross-sectional, observational study
Abstract
Background: Neonatal deaths now account for 47% of all deaths in children younger than 5 years globally. More than a third of newborn deaths are due to preterm birth complications, which is the leading cause of death. Understanding the causes and factors contributing to neonatal deaths is needed to identify interventions that will reduce mortality. We aimed to establish the major causes of preterm mortality in preterm infants in the first 28 days of life in Ethiopia.
Methods: We did a prospective, cross-sectional, observational study in five hospitals in Ethiopia. Study participants were preterm infants born in the study hospitals at younger than 37 gestational weeks. Infants whose gestational age could not be reliably estimated and those born as a result of induced abortion were excluded from the study. Data were collected on maternal and obstetric history, clinical maternal and neonatal conditions, and laboratory investigations. For neonates who died of those enrolled, consent was requested from parents for post-mortem examinations (both complete diagnostic autopsy and minimally invasive tissue sampling). An independent panel of experts established the primary and contributory causes of preterm mortality with available data.
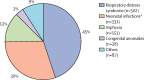
Findings: Between July 1, 2016, to May 31, 2018, 4919 preterm infants were enrolled in the study and 3852 were admitted to neonatal intensive care units. By 28 days of post-natal age, 1109 (29%) of those admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit died. Complete diagnostic autopsy was done in 441 (40%) and minimally invasive tissue sampling in 126 (11%) of the neonatal intensive care unit deaths. The main primary causes of death in the 1109 infants were established as respiratory distress syndrome (502 [45%]); sepsis, pneumonia and meningitis (combined as neonatal infections; 331 [30%]), and asphyxia (151 [14%]). Hypothermia was the most common contributory cause of preterm mortality (770 [69%]). The highest mortality occurred in infants younger than 28 weeks of gestation (89 [86%] of 104), followed by infants aged 28-31 weeks (512 [54%] of 952), 32-34 weeks (349 [18%] of 1975), and 35-36 weeks (159 [8%] of 1888).
Interpretation: Three conditions accounted for 89% of all deaths among preterm infants in Ethiopia. Scale-up interventions are needed to prevent or treat these conditions. Further research is required to develop effective and affordable interventions to prevent and treat the major causes of preterm death.
Funding: Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY 4.0 license. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Understanding the causes of preterm birth: solutions depend on context.Lancet Glob Health. 2019 Aug;7(8):e1000-e1001. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(19)30281-5. Lancet Glob Health. 2019. PMID: 31303282 No abstract available.
References
-
- Behrman RE, Butler AS, editors. Mortality and acute complications in preterm infants. National Academies Press; Washington DC: 2007.
-
- UNICEF. WHO. World Bank. UN-DESA Population Division Levels and trends in child mortality report 2017. 2018. Estimates developed by the UN inter-agency group for child mortality estimation. http://www.who.int/maternal_child_adolescent/documents/levels_trends_chi...
-
- WHO Preterm birth Key facts. 2018. http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/preterm-birth
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous