Kidney Complications of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Review
- PMID: 31303350
- PMCID: PMC6756976
- DOI: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2019.03.433
Kidney Complications of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Review
Abstract
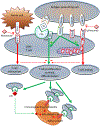
Immunologic control of malignancy has long been recognized as an important determinant of disease progression. Recent advances in immunology have led to the focus on several mechanisms that can be targeted to achieve tumor suppression. In particular, checkpoint inhibition has evolved in less than a decade to become one of the most important strategies in cancer therapy, with a meaningful improvement in patient survival. Six agents have been approved for clinical use to date and many more are in the industry pipeline. The spectrum of malignancies responsive to immunotherapy ranges from advanced melanoma, for which the first immune checkpoint inhibitor ipilimumab was approved, to Hodgkin lymphoma, non-small cell lung cancer, renal cell carcinoma, and others. Notwithstanding its clinical benefits, checkpoint inhibition carries a risk for significant off-target toxicity stemming from the immune system activation. In this review, we discuss general principles of checkpoint inhibition, mechanisms of toxicity, and kidney complications of the treatment and propose diagnostic and treatment strategies when kidney injury occurs.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury (AKI); cancer immunotherapy; checkpoint inhibitor; corticosteroids; cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated protein 4 inhibitor; immune-related adverse effect (irAE); immunotherapy; interstitial nephritis; onconephrology; programmed cell death protein 1 inhibitor; renal function; review.
Copyright © 2019 National Kidney Foundation, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Abelson HT, Fosburg MT, Beardsley GP, Goorin AM, Gorka C, Link M, et al. Methotrexate-induced renal impairment: clinical studies and rescue from systemic toxicity with high-dose leucovorin and thymidine. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 1983;1(3):208–16. - PubMed
-
- Izzedine H, Launay-Vacher V, Isnard-Bagnis C, Deray G. Drug-induced Fanconi's syndrome. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003;41(2):292–309. - PubMed
-
- Izzedine H, Massard C, Spano JP, Goldwasser F, Khayat D, Soria JC. VEGF signalling inhibition-induced proteinuria: Mechanisms, significance and management. Eur J Cancer. 2010;46(2):439–48. - PubMed
-
- Hansen SW, Groth S, Daugaard G, Rossing N, Rorth M. Long-term effects on renal function and blood pressure of treatment with cisplatin, vinblastine, and bleomycin in patients with germ cell cancer. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 1988;6(11):1728–31. - PubMed
-
- Hingorani S, Guthrie KA, Schoch G, Weiss NS, McDonald GB. Chronic kidney disease in long-term survivors of hematopoietic cell transplant. Bone marrow transplantation. 2007;39(4):223–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

