Loss of Function of Phosphodiesterase 11A4 Shows that Recent and Remote Long-Term Memories Can Be Uncoupled
- PMID: 31303492
- PMCID: PMC6709976
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2019.06.018
Loss of Function of Phosphodiesterase 11A4 Shows that Recent and Remote Long-Term Memories Can Be Uncoupled
Abstract
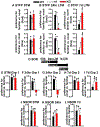
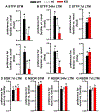
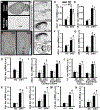
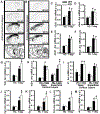
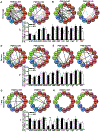
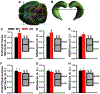
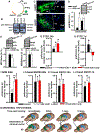
Systems consolidation is a process by which memories initially require the hippocampus for recent long-term memory (LTM) but then become increasingly independent of the hippocampus and more dependent on the cortex for remote LTM. Here, we study the role of phosphodiesterase 11A4 (PDE11A4) in systems consolidation. PDE11A4, which degrades cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) and cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), is preferentially expressed in neurons of CA1, the subiculum, and the adjacently connected amygdalohippocampal region. In male and female mice, deletion of PDE11A enhances remote LTM for social odor recognition and social transmission of food preference (STFP) despite eliminating or silencing recent LTM for those same social events. Measurement of a surrogate marker of neuronal activation (i.e., Arc mRNA) suggests the recent LTM deficits observed in Pde11 knockout mice correspond with decreased activation of ventral CA1 relative to wild-type littermates. In contrast, the enhanced remote LTM observed in Pde11a knockout mice corresponds with increased activation and altered functional connectivity of anterior cingulate cortex, frontal association cortex, parasubiculum, and the superficial layer of medial entorhinal cortex. The apparent increased neural activation observed in prefrontal cortex of Pde11a knockout mice during remote LTM retrieval may be related to an upregulation of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunits NR1 and NR2A. Viral restoration of PDE11A4 to vCA1 alone is sufficient to rescue both the LTM phenotypes and upregulation of NR1 exhibited by Pde11a knockout mice. Together, our findings suggest remote LTM can be decoupled from recent LTM, which may have relevance for cognitive deficits associated with aging, temporal lobe epilepsy, or transient global amnesia.
Keywords: Kamin effect; cGMP; consolidation; cyclic nucleotide; memory lapse; phosphodiesterase; remote memory; system consolidation; systems consolidation; transient amnesia.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Frankland PW, and Bontempi B (2005). The organization of recent and remote memories. Nat Rev Neurosci 6, 119–130. - PubMed
-
- Tonegawa S, Morrissey MD, and Kitamura T (2018). The role of engram cells in the systems consolidation of memory. Nat Rev Neurosci 19, 485–498. - PubMed
-
- Kogan JH, Frankland PW, and Silva AJ (2000). Long-term memory underlying hippocampus-dependent social recognition in mice. Hippocampus 10, 47–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

