Effect of 12-week home-based cognitive training on cognitive function and brain metabolism in patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment
- PMID: 31303750
- PMCID: PMC6610290
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S200269
Effect of 12-week home-based cognitive training on cognitive function and brain metabolism in patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment
Abstract
Purpose: We assessed the effect of home-based cognitive intervention (HCI) on cognitive function along with brain metabolism by 18F-FDG PET in patients with amnestic MCI (aMCI).
Patients and methods: Fifty-seven patients with aMCI from three hospitals were randomized (30 HCI, 27 control). For 12 weeks, subjects received HCI. Thirty-two subjects (15 HCI, 17 control) underwent brain 18-F-FDG-PET imaging at baseline and at 12 and 24 weeks.
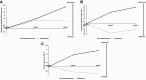
Results: The HCI group showed significant improvement in the scores of the Controlled Oral Word Association Test (COWAT) 12 and at 24 weeks. Significant brain metabolic changes by 18F-FDG PET were not observed.
Conclusion: The current study suggests that HCI was effective in improving general cognition along with frontal executive function in patients with aMCI.
Keywords: brain PET; cognitive training; mild cognitive impairment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
FDG-PET in the Evaluation of Brain Metabolic Changes Induced by Cognitive Stimulation in aMCI Subjects.Curr Radiopharm. 2015;8(1):69-75. doi: 10.2174/1874471008666150428122924. Curr Radiopharm. 2015. PMID: 25925343
-
Biomarker-Based Prediction of Progression to Dementia: F-18 FDG-PET in Amnestic MCI.Neurol India. 2019 Sep-Oct;67(5):1310-1317. doi: 10.4103/0028-3886.271245. Neurol India. 2019. PMID: 31744965
-
Effects of a 6-month cognitive intervention on brain metabolism in patients with amnestic MCI and mild Alzheimer's disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2011;26 Suppl 3:337-48. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2011-0025. J Alzheimers Dis. 2011. PMID: 21971473 Clinical Trial.
-
Brain metabolism and cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers profile of non-amnestic mild cognitive impairment in comparison to amnestic mild cognitive impairment and normal older subjects.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2015 Sep 15;7(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s13195-015-0143-0. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 26373380 Free PMC article.
-
T and B cell subsets differentially correlate with amyloid deposition and neurocognitive function in patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment after one year of physical activity.Exerc Immunol Rev. 2019;25:34-49. Exerc Immunol Rev. 2019. PMID: 30785868 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
[Long-term effect analysis of a cognitive stimulation program in mild cognitive impairment elderly in Primary Care: A randomized controlled trial].Aten Primaria. 2021 Aug-Sep;53(7):102053. doi: 10.1016/j.aprim.2021.102053. Epub 2021 Apr 14. Aten Primaria. 2021. PMID: 33865010 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. Spanish.
-
Cognitive Intervention with Musical Stimuli Using Digital Devices on Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Pilot Study.Healthcare (Basel). 2020 Feb 25;8(1):45. doi: 10.3390/healthcare8010045. Healthcare (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32106559 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies to Promote Cognitive Health in Aging: Recent Evidence and Innovations.Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2022 Sep;24(9):441-450. doi: 10.1007/s11920-022-01348-x. Epub 2022 Jul 15. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2022. PMID: 35835897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Efficacy of a Home-Based, Augmented Reality Dual-Task Platform for Cognitive-Motor Training in Elderly Patients: A Pilot Observational Study.Psychiatry Investig. 2024 Oct;21(10):1045-1053. doi: 10.30773/pi.2024.0103. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Psychiatry Investig. 2024. PMID: 39344368 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive Interventions: Symptomatic or Disease-Modifying Treatments in the Brain?JAR Life. 2024 May 22;13:60-64. doi: 10.14283/jarlife.2024.8. eCollection 2024. JAR Life. 2024. PMID: 38808149 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

