Stereoelectroencephalography in epilepsy, cognitive neurophysiology, and psychiatric disease: safety, efficacy, and place in therapy
- PMID: 31303757
- PMCID: PMC6610288
- DOI: 10.2147/NDT.S177804
Stereoelectroencephalography in epilepsy, cognitive neurophysiology, and psychiatric disease: safety, efficacy, and place in therapy
Abstract
For patients with drug-resistant epilepsy, surgical intervention may be an effective treatment option if the epileptogenic zone (EZ) can be well localized. Subdural strip and grid electrode (SDE) implantations have long been used as the mainstay of intracranial seizure localization in the United States. Stereoelectroencephalography (SEEG) is an alternative approach in which depth electrodes are placed through percutaneous drill holes to stereotactically defined coordinates in the brain. Long used in certain centers in Europe, SEEG is gaining wider popularity in North America, bolstered by the advent of stereotactic robotic assistance and mounting evidence of safety, without the need for catheter-based angiography. Rates of clinically significant hemorrhage, infection, and other complications appear lower with SEEG than with SDE implants. SEEG also avoids unnecessary craniotomies when seizures are localized to unresectable eloquent cortex, found to be multifocal or nonfocal, or ultimately treated with stereotactic procedures such as laser interstitial thermal therapy (LITT), radiofrequency thermocoagulation (RF-TC), responsive neurostimulation (RNS), or deep brain stimulation (DBS). While SDE allows for excellent localization and functional mapping on the cortical surface, SEEG offers a less invasive option for sampling disparate brain areas, bilateral investigations, and deep or medial targets. SEEG has shown efficacy for seizure localization in the temporal lobe, the insula, lesional and nonlesional extra-temporal epilepsy, hypothalamic hamartomas, periventricular nodular heterotopias, and patients who have had prior craniotomies for resections or grids. SEEG offers a valuable opportunity for cognitive neurophysiology research and may have an important role in the study of dysfunctional networks in psychiatric disease and understanding the effects of neuromodulation.
Keywords: SEEG; cognitive neurophysiology; epilepsy surgery; psychiatric neurosurgery; stereoelectroencephalography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
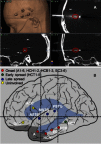
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

