Discovery of (aza)indole derivatives as novel respiratory syncytial virus fusion inhibitors
- PMID: 31303995
- PMCID: PMC6596086
- DOI: 10.1039/c9md00178f
Discovery of (aza)indole derivatives as novel respiratory syncytial virus fusion inhibitors
Abstract
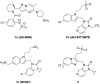
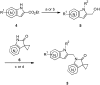
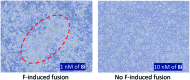
A new class of indole derivatives (3) have been identified as potent RSV fusion inhibitors. SAR exploration revealed that 5-Cl and the sulfonyl side chain of the indole scaffold are crucial for anti-RSV activity. Further optimization led to the discovery of a cyclic sulfone (8i) with 2 nM anti-RSV activity and a much improved PK profile compared to the non-cyclic sulfone counterpart.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Discovery of methylsulfonyl indazoles as potent and orally active respiratory syncytial Virus(RSV) fusion inhibitors.Eur J Med Chem. 2017 Sep 29;138:1147-1157. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.07.032. Epub 2017 Jul 20. Eur J Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28772235
-
Discovery of Benzoazepinequinoline (BAQ) Derivatives as Novel, Potent, Orally Bioavailable Respiratory Syncytial Virus Fusion Inhibitors.J Med Chem. 2018 Nov 21;61(22):10228-10241. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b01394. Epub 2018 Nov 2. J Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 30339388
-
Discovery of Piperazinylquinoline Derivatives as Novel Respiratory Syncytial Virus Fusion Inhibitors.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2016 Apr 20;7(6):558-62. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.5b00234. eCollection 2016 Jun 9. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2016. PMID: 27326326 Free PMC article.
-
Respiratory syncytial virus vaccine: where are we now and what comes next?Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2018 Dec;18(12):1247-1256. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2018.1544239. Epub 2018 Nov 14. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2018. PMID: 30426788 Review.
-
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) evades the human adaptive immune system by skewing the Th1/Th2 cytokine balance toward increased levels of Th2 cytokines and IgE, markers of allergy--a review.Virus Genes. 2006 Oct;33(2):235-52. doi: 10.1007/s11262-006-0064-x. Virus Genes. 2006. PMID: 16972040 Review.
References
-
- Ding W. D., Mitsner B., Krishnamurthy G., Aulabaugh A., Hess C. D., Zaccardi J., Cutler M., Feld B., Gazumyan A., Raifeld Y., Antonia Nikitenko A., Lang S. A., Gluzman Y., O'Hara B., Ellestad G. A. J. Med. Chem. 1998;41:2671–2675. - PubMed
- Andries K., Moeremans M., Gevers T., Willebrords R., Sommen C., Lacrampe J., Janssens F., Wyde P. R. Antiviral Res. 2003;60:209–219. - PubMed
- Bonfanti J. F., Meyer C., Doublet F., Fortin J., Muller P., Queguiner L., Gevers T., Janssens P., Szel H., Willebrords R., Timmerman P., Wuyts K., van Remoortere P., Janssens F., Wigerinck P., Andries K. J. Med. Chem. 2008;51:875–896. - PubMed
- Yu K. L., Sin N., Civiello R. L., Wang X. A., Combrink K. D., Gulgeze H. B. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007;17:895. - PubMed
- Sun Z., Pan Y., Jiang S., Lu L. Viruses. 2013;5:211–225. - PMC - PubMed
- Mackman R. L., Sangi M., Sperandio D., Parrish J. P., Eisenberg E., Perron M. J. Med. Chem. 2015;58:1630–1643. - PubMed
- ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT01756482.
- Roymans D., Alnajjar S. S., Battles M. B., Sitthicharoenchai P., Furmanova-Hollenstein P., Rigaux P., Berg J. V. D., Kwanten L., Ginderen M. V., Verheyen N., Vranckx L., Jaensch S., Arnoult E., Voorzaat R., Gallup J. M., Larios-Mora A., Crabbe M., Huntjens D., Raboisson P., Langedijk J. P., Ackermann M. R., McLellan J. S., Vendeville S., Koul A. Nat. Commun. 2017;8:167. - PMC - PubMed
- Cockerill G. S., Good J. A. D., Mathews N. J. Med. Chem. 2019;62:3206–3227. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

