Role of blood glucose and fat profile in lung function pattern of Indian type 2 diabetic subjects
- PMID: 31304013
- PMCID: PMC6600883
- DOI: 10.1186/s40248-019-0184-5
Role of blood glucose and fat profile in lung function pattern of Indian type 2 diabetic subjects
Abstract
Background and objectives: It has been hypothesized that changes in lung function can occur in patients with diabetes. Nevertheless, it is unclear how much of this correlation links with biomarkers of metabolism disorder. We have investigated the association between hypoglycaemic and fat profile with lung function in Indian diabetic subjects.
Design: Prospective observational study.
Setting: Diabetes care unit of King Edward Memorial (KEM) hospital.
Patients: Out of 465 patients who agreed to participate in this study, valid lung function data were available from 347 Type 2 diabetic subjects.
Measurements: Pulmonary function test including predicted forced vital capacity (% FVC), predicted forced expiratory volume in 1 second (% FEV1) and FEV1/FVC ratio were assessed. We also examined fat profile, glucose, HbA1c, hemoglobin and other hematological parameters.
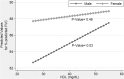
Results: Four hundred sixty-five subjects aged 55 ± 11 participated in the study. Predicted forced vital capacity, % FEV1 and FEV1/FVC ratio was 85.88 ± 13.53, 85.87 ± 14.06 and 82.03 ± 6.83, respectively. Also, approximately 8 to 17% of the participant reported having at least one chronic respiratory symptom or lung disease. We found that high glycaemic measures (i.e. fasting and post-meal plasma glucose) are linked with dyspnea. In addition, HDL (high-density lipoprotein) concentration was directly associated with % FVC.
Conclusions: It is difficult to draw a clear conclusion about the cause-effect relationship or clinical impact based on this study alone. However, identification of clinically meaningful elements for developing a screening program is critical.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus; Fat profile; risk factors; Hyperglycaemia; Respiratory distress syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests. SS is member of the Editorial Board of Multidisciplinary Respiratory Medicine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effect of alogliptin on pulmonary function in obese patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled by metformin monotherapy.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Aug;95(33):e4541. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000004541. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27537577 Free PMC article.
-
Glycemic disorders and their impact on lung function. Cross-sectional study.Med Clin (Barc). 2019 Nov 29;153(10):387-390. doi: 10.1016/j.medcli.2018.08.003. Epub 2018 Oct 9. Med Clin (Barc). 2019. PMID: 30309667 English, Spanish.
-
Association between Lung Function and New-Onset Diabetes Mellitus in Healthy Individuals after a 6-Year Follow-up.Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2021 Dec;36(6):1254-1267. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2021.1249. Epub 2021 Dec 13. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2021. PMID: 34897261 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between pulmonary function and albuminuria in type 2 diabetic patients with preserved renal function.BMC Endocr Disord. 2020 Jul 23;20(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s12902-020-00598-1. BMC Endocr Disord. 2020. PMID: 32703207 Free PMC article.
-
[Evaluation of respiratory function tests in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes].Pediatr Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2012;18(1):15-20. Pediatr Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2012. PMID: 22525686 Polish.
Cited by
-
Linear effects of glucose levels on voice fundamental frequency in type 2 diabetes and individuals with normoglycemia.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 28;14(1):19012. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-69620-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39198592 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Pulmonary Functions and Dysfunctions in Type II Diabetes Mellitus: A Comparative Cross-Sectional Study.Cureus. 2023 Feb 16;15(2):e35081. doi: 10.7759/cureus.35081. eCollection 2023 Feb. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 36945284 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hills AP, Misra A, Gill JMR, Byrne NM, Soares MJ, Ramachandran A, Palaniappan L, Street SJ, Jayawardena R, Khunti K, et al. Public health and health systems: implications for the prevention and management of type 2 diabetes in South Asia. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018;6(12):992–1002. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(18)30203-1. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources