The hybrid emergency room system: a novel trauma evaluation and care system created in Japan
- PMID: 31304025
- PMCID: PMC6603312
- DOI: 10.1002/ams2.412
The hybrid emergency room system: a novel trauma evaluation and care system created in Japan
Abstract
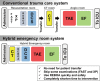
The ultimate trauma management system should allow the completion of all time-consuming life-saving procedures in one trauma resuscitation room. In 2011, the Hybrid Emergency Room System (HERS) was developed in Japan as a novel trauma care system that allows clinicians to perform all life-saving procedures for severely injured patients, including whole-body computed tomography examination, damage control surgery, and transcatheter arterial embolization by interventional radiology, on the same table in the same room without transferring the patient. Since then, the number of HERS installations has rapidly increased around Japan. To promote further innovation and dissemination of this new and creative concept of trauma management, the Japanese Association for Hybrid Emergency Room System was launched on June 21, 2018. In this article, the concept, history, and current evidence behind this new trauma workflow system are summarized. This is the first review to show the next direction of trauma care using HERS.
Keywords: Computed tomography; interventional radiology; patient care management; severe trauma; surgery.
Figures

Similar articles
-
First installation of a dual-room IVR-CT system in the emergency room.Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2018 Mar 5;26(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s13049-018-0484-3. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2018. PMID: 29506552 Free PMC article.
-
First establishment of a new table-rotated-type hybrid emergency room system.Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2018 Sep 17;26(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s13049-018-0532-z. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2018. PMID: 30223859 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Survival Benefit of a Novel Trauma Workflow that Includes Immediate Whole-body Computed Tomography, Surgery, and Interventional Radiology, All in One Trauma Resuscitation Room: A Retrospective Historical Control Study.Ann Surg. 2019 Feb;269(2):370-376. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002527. Ann Surg. 2019. PMID: 28953551 Free PMC article.
-
Hybrid emergency room: Installation, establishment, and innovation in the emergency department.Acute Med Surg. 2023 May 31;10(1):e856. doi: 10.1002/ams2.856. eCollection 2023 Jan-Dec. Acute Med Surg. 2023. PMID: 37266185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Time to Hemorrhage Control in a Hybrid ER System: Is It Time to Change?Shock. 2021 Dec 1;56(1S):16-21. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000001539. Shock. 2021. PMID: 32205794
Cited by
-
Hybrid emergency room management of a ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm.J Vasc Surg Cases Innov Tech. 2020 Dec 28;7(1):21-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jvscit.2020.12.006. eCollection 2021 Mar. J Vasc Surg Cases Innov Tech. 2020. PMID: 33665526 Free PMC article.
-
Blunt thoracic aortic injury treated with thoracic endovascular aortic repair in hybrid emergency room: A case report.Trauma Case Rep. 2025 Jan 4;55:101124. doi: 10.1016/j.tcr.2025.101124. eCollection 2025 Feb. Trauma Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 39872423 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of a hybrid emergency room system in the management of acute ischemic stroke: a single-center experience.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Jul 4;11:1420951. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1420951. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39026550 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence of acute aortic dissections in patients with out of hospital cardiac arrest: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies.Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2021 Dec 23;38:100934. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2021.100934. eCollection 2022 Feb. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2021. PMID: 35005212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perioperative Management of Polytrauma Patients with Severe Traumatic Brain Injury Undergoing Emergency Extracranial Surgery: A Narrative Review.J Clin Med. 2021 Dec 21;11(1):18. doi: 10.3390/jcm11010018. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 35011760 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Weninger P, Mauritz W, Fridrich P et al Emergency room management of patients with blunt major trauma: evaluation of the multislice computed tomography protocol exemplified by an urban trauma center. J. Trauma 2007; 62: 584–91. - PubMed
-
- Hilbert P, zur Nieden K, Hofmann GO, Hoeller I, Koch R, Stuttmann R. New aspects in the emergency room management of critically injured patients: a multi‐slice CT‐oriented care algorithm. Injury 2007;38:552–8. - PubMed
-
- Fung Kon Jin PH, Goslings JC, Ponsen KJ, van Kuijk C, Hoogerwerf N, Luitse JS. Assessment of a new trauma workflow concept implementing a sliding CT scanner in the trauma room: the effect on workup times. J. Trauma 2008;64:1320–6. - PubMed
-
- Lee KL, Graham CA, Lam JM, Yeung JH, Ahuja AT, Rainer TH. Impact on trauma patient management of installing a computed tomography scanner in the emergency department. Injury 2009; 40: 873–5. - PubMed
-
- Hughes J, Scrimshire A, Steinberg L et al Interventional Radiology service provision and practice for the management of traumatic splenic injury across the Regional Trauma Networks of England. Injury 2017; 48: 1031–4. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

