A longitudinal study of neurocognition and behavior in patients with Hurler-Scheie syndrome heterozygous for the L238Q mutation
- PMID: 31304092
- PMCID: PMC6603334
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymgmr.2019.100484
A longitudinal study of neurocognition and behavior in patients with Hurler-Scheie syndrome heterozygous for the L238Q mutation
Abstract
Previous research has demonstrated the mutation, c.712T>A (p.L238Q) of the gene for α-L- iduronidase (IDUA) in patients with Hurler-Scheie syndrome is relatively severe when paired with a nonsense or deletion or splice-site mutation. This mutation was also found to be associated with psychiatric symptoms. This research presents longitudinal data and protein analysis to further investigate the severity and natural history of these unique patients.
Methods: Six patients heterozygous for L238Q were compared to six patients with Hurler-Scheie without the L238Q mutations. Somatic burden of disease, IQ, memory, attention, adaptive functioning and behavioral measures were given yearly over 2 to 4 years from 2009 to 2014. The impact of L238Q on the IDUA enzyme was examined using 7 bioinformatics tools and a 3D structural analysis.
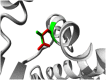
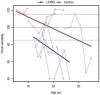
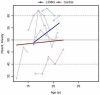
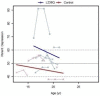
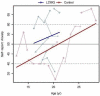
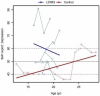
Results: Similar to the cross sectional study, the L238Q patients had more severe abnormalities in IQ, attention, adaptive functioning, and behavioral functioning than the comparison group. There were no major differences between the two groups in change over time; IQ for both groups was stable with some behavioral areas showing improvement. Over time, both groups declined in visual spatial memory and, attention/visual processing. They also showed increased anxiety. Structural and bioinformatics analysis of the L238Q suggest that this mutation causes a significant reduction in the IDUA enzyme's potential catalytic activity, and this mutation may be more severe than other mutations contributing to the Hurler-Scheie syndrome phenotype, presumably causing the psychiatric disease.
Conclusion: L238Q patients demonstrate severe neurocognitive and neurobehavioral deficits but are relatively stable. Like the comparison group, decreasing visual spatial memory and attention and increasing anxiety suggest more intervention in life skills and emotional social supports are needed.
Keywords: Hurler-Scheie syndrome; L238Q mutation; Mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS); Neurocognition; α-L-iduronidase.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Neurocognitive and neuropsychiatric phenotypes associated with the mutation L238Q of the α-L-iduronidase gene in Hurler-Scheie syndrome.Mol Genet Metab. 2014 Feb;111(2):123-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2013.11.014. Epub 2013 Dec 12. Mol Genet Metab. 2014. PMID: 24368159 Free PMC article.
-
Novel splice site IDUA gene mutation in Tunisian pedigrees with hurler syndrome.Diagn Pathol. 2018 May 29;13(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s13000-018-0710-3. Diagn Pathol. 2018. PMID: 29843745 Free PMC article.
-
Residual α-L-iduronidase activity in fibroblasts of mild to severe Mucopolysaccharidosis type I patients.Mol Genet Metab. 2013 Aug;109(4):377-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2013.05.016. Epub 2013 Jun 4. Mol Genet Metab. 2013. PMID: 23786846
-
Molecular genetics of mucopolysaccharidosis type I: diagnostic, clinical, and biological implications.Hum Mutat. 1995;6(4):288-302. doi: 10.1002/humu.1380060403. Hum Mutat. 1995. PMID: 8680403 Review.
-
Mucopolysaccharidosis type I.Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2014 Sep;12 Suppl 1:102-6. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2014. PMID: 25345091 Review.
Cited by
-
Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I Diagnosed by Aortic and Mitral Valve Replacement.JACC Case Rep. 2021 Dec 15;3(18):1891-1894. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2021.10.013. eCollection 2021 Dec 15. JACC Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34984346 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yogalingam G., Guo X.H., Muller V.J., Brooks D.A., Clements P.R., Kakkis E.D., Hopwood J.J. Identification and molecular characterization of α-L-iduronidase mutations present in mucopolysaccharidosis type I patients undergoing enzyme replacement therapy. Hum. Mutat. 2004;24:199–207. - PubMed
-
- Chandar S.S., Mahalingam K. Mucopolysaccharidosis type I: homology Modeling and docking analysis of the lysosomal enzyme, human α-L-iduronidase. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2012;6(27):2027–2038.
-
- Saito S., Ohno K., Maita N., Sakuraba H. Structural and clinical implications of amino acid substitutions in α-L-iduronidase: insight into the basis of mucopolysaccharidosis type I. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2014 Feb;111(2):107–112. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed Alia, Whitley Chester B., Cooksley Renee, Rudser Kyle, Cagle Stephanie, Ali Nadia, Delaney Kathleen, Yund Brianna, Shapiro Elsa. Neurocognitive and neuropsychiatric phenotypes associated with the mutation L238Q of the α-L-iduronidase gene in Hurler-Scheie syndrome. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2014 Feb;111(2):123–127. (PMCID: PMC3939822) - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

