Development and validation of a deep learning algorithm for improving Gleason scoring of prostate cancer
- PMID: 31304394
- PMCID: PMC6555810
- DOI: 10.1038/s41746-019-0112-2
Development and validation of a deep learning algorithm for improving Gleason scoring of prostate cancer
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Publisher Correction: Development and validation of a deep learning algorithm for improving Gleason scoring of prostate cancer.NPJ Digit Med. 2019 Nov 19;2:113. doi: 10.1038/s41746-019-0196-8. eCollection 2019. NPJ Digit Med. 2019. PMID: 31754638 Free PMC article.
Abstract
For prostate cancer patients, the Gleason score is one of the most important prognostic factors, potentially determining treatment independent of the stage. However, Gleason scoring is based on subjective microscopic examination of tumor morphology and suffers from poor reproducibility. Here we present a deep learning system (DLS) for Gleason scoring whole-slide images of prostatectomies. Our system was developed using 112 million pathologist-annotated image patches from 1226 slides, and evaluated on an independent validation dataset of 331 slides. Compared to a reference standard provided by genitourinary pathology experts, the mean accuracy among 29 general pathologists was 0.61 on the validation set. The DLS achieved a significantly higher diagnostic accuracy of 0.70 (p = 0.002) and trended towards better patient risk stratification in correlations to clinical follow-up data. Our approach could improve the accuracy of Gleason scoring and subsequent therapy decisions, particularly where specialist expertise is unavailable. The DLS also goes beyond the current Gleason system to more finely characterize and quantitate tumor morphology, providing opportunities for refinement of the Gleason system itself.
Keywords: Prostate cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsK.N., D.F., Y.L., P.-H.C.C., E.W., F.T., G.S.C., R.M.D., L.H.P., C.H.M., J.D.H. and M.C.S. are employees of Google LLC and own Alphabet stock.
Figures



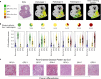
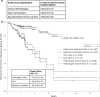
Comment in
-
Next generation diagnostic pathology: use of digital pathology and artificial intelligence tools to augment a pathological diagnosis.Diagn Pathol. 2019 Dec 27;14(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s13000-019-0921-2. Diagn Pathol. 2019. PMID: 31881972 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Prostate Cancer—Cancer Stat Facts. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/prost.html. Accessed 22 August 2018.
-
- Epstein, J. I. et al. The 2014 International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Consensus Conference on Gleason Grading of Prostatic Carcinoma: Definition of Grading Patterns and Proposal for a New Grading System. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 40, 244–252 (2016). - PubMed
-
- NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/default.aspx#prostate. Accessed 14 August 2018.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

